I. Introduction
II. Origin of the Problem
A. The Legacy of the Cold War and Early Failures to Protect the
Environment
B. Addressing Real Risks to Real Communities
C. The
History of Federal Facility Cleanup
D. Renewing the Commitment to
Cleanup
III. Owning up to the Federal Responsibility
A. Survey of Agency Challenges
B. Building Knowledge About
Relative Risk at Sites
C. DOD: A Relative Risk Framework and Community
Partnerships
D. DOE: Ongoing Process Improvements
IV. Paying the Cold War Mortgage: Remaining Challenges
A. The Potential Funding Gap
B. Historical Management Obstacles
to DOE Program Improvement
C. The Need for Statutory and Regulatory Reform
D. The Special Problems of Radioactive Waste
E. The Need to Develop
and Implement More Cost-Effective Technology
V. The Path to Reform
A. Principles of Reform
B. Statutory Reform
C. Administrative and
Regulatory Reform
D. Management Reform
E. Cost-Effective Technology
Development and Implementation
F. Budget Process Reform
Glossary
The environmental cleanup of Federal lands and facilities would pose enormous scientific, technical, administrative, regulatory, and political challenges, even if resources available for this purpose were unlimited. As the Federal government works to reduce spending to eliminate the Federal budget deficit, all Federal programs must compete for a shrinking pool of discretionary resources. This reduction in resources requires concerted action to maximize the net benefits achieved from every dollar invested in Federal facilities cleanup. There is general consensus that this objective requires far more rigorous risk-based priority setting and management improvement, both within and across sites, than have been achieved to date, as well as statutory and regulatory reforms to remove impediments to success. The ability of policy makers, program managers, regulators and other stakeholders collectively to define and carry out specific reforms will determine whether the Nation's multi-billion dollar investment in Federal facilities cleanup succeeds or fails.
This report presents the analysis, conclusions, and recommendations of the Federal Facilities Policy Group (FFPG), convened by the Director of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the Chair of the Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) to review the current status and future course of environmental response and restoration at Federal facilities. Specifically, this report identifies areas of management and regulatory reform essential to protect public health and restore the environment, as well as to assure effective, efficient use of resources as the effort to clean up Federal facilities proceeds.
A. The Legacy of the Cold War and Early Failures to Protect the Environment.
Over the last 25 years, public awareness of the human health and environmental hazards associated with the release of toxic, hazardous, and radiological substances has grown dramatically. The worst hazardous waste problems, such as the Love Canal site in New York, focused public attention on the lack of adequate Federal regulation and resources to guard against the future release of hazardous substances or to address cleanup of sites already contaminated. From the late 1970s onward, these concerns generated an array of Federal responses designed to hold responsible parties accountable for the proper handling and disposal of hazardous materials while also providing for the cleanup of existing contamination.
Lack of sensitivity to environmental protection by some agencies was also a problem on Federal lands and Federal facilities around the country. For some agencies, the sense of urgency to develop a stockpile of nuclear weapons and maintain a prepared military force during the Cold War, coupled with the secrecy and compartmentalization of information required for nuclear technology security, resulted in long delays before significant environmental problems were understood or addressed. Consequently, the extent of existing contamination on Federal land is only now being fully characterized and the enormity of the cleanup challenge adequately recognized.
B. Addressing Real Risks to Real Communities.
Federal leadership in meeting the cleanup challenge and making appropriate cleanup decisions for the diverse portfolio of sites under Federal management is a legal and economic imperative. Some of these hazardous waste sites present a risk to public health and the environment for communities serving as hosts to essential government missions, such as weapons production and some defense operations. The Clinton Administration recognizes a moral commitment to these communities, and to current and future generations, to address the risks posed by hazardous substances at these facilities. Successive Congresses have translated this imperative into a legal mandate, reflected in a host of specific environmental compliance obligations imposed by statute on Federal agencies. The economic significance of these obligations is increasing, because efficient and effective cleanup decisions at these facilities are necessary to meet targets for reduced Federal spending and to facilitate the environmental and economic redevelopment and beneficial reuse of Federal facilities. This is especially important as the closure of Department of Defense (DOD) bases and the overall reduction in the number of agency facilities renders large numbers of facilities available for economic redevelopment or transfer to other Federal uses.
Although there is consensus on the obligation to address contamination at Federal facility sites, there is insufficient agreement on the scope of the obligation or the appropriate standards to guide decisions about remediation, restoration, and future use of Federal agency sites. Indeed, the magnitude of the challenges presented by the commitment to address the numerous, diverse, and complex environmental problems at Federal facilities underscores the importance of making the best possible judgments concerning risk, priority, cost, and cleanup levels. Yet, even as our knowledge about sites has improved, there remains considerable debate and little consensus concerning the precise nature and severity of risks presented at certain Federal facility sites, the standards that should apply in determining cleanup levels, the priority and pace of cleaning up the portfolios of sites managed by each agency, and the role of costs and benefits in developing and constraining cleanup strategies.
C. The History of Federal Facility Cleanup.
The 1980s, the first full decade of effort by Federal agencies to address contamination at their facilities, yielded little actual cleanup until the end of the decade. The Cold War secrecy that shrouded a number of Federal facilities hindered rapid assessment of the environmental conditions at those sites. At some agencies, environmental protection and restoration were not given priority among other competing agency missions. Further, the lack of a separate environmental function and expertise within agencies, or of a clear mandate for environmental awareness in the performance of mission activities, hampered commitment and effort during these years. Some agencies bridged this gap with a heavy reliance on contractors, at times with losses in accountability and failure to control costs.
1. Knowledge, Technology and Communication Limitations.
These difficulties were compounded by very real limitations on public knowledge, technology, and communication -- a number of which still exist today. At the inception of their remedial programs in the early 1980s, agencies knew little about the extent and nature of their contamination problems or about the relative risks and priorities among sites. Cleanup technologies often were unavailable, and, in important instances, are still in early stages of development. Some agencies also had little experience in communicating effectively with local communities and other stakeholders due to their long history of secrecy at many sites. These communication difficulties contributed to further public distrust of operations at those Federal facilities and to a lack of public confidence in the Federal commitment to eventual cleanup of Federal lands.
2. Early Responses.
Although creation of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 1970 is widely recognized as the start of the Federal environmental movement, the lack of sustained commitment, the lack of a steady funding stream for Federal facilities cleanup, the slow pace of cleanup, and the failure by Federal agencies to communicate with communities that characterized the early Federal cleanup effort, prompted strong legislative responses. The Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA or Superfund) was amended in 1986 to include deadlines for the assessment of Federal facilities and enhanced enforcement tools by which the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and other regulators could compel cleanup at Federal agency sites. These tools included a requirement that responsible agencies enter interagency agreements (IAGS) with regulators. These enforcement tools were later supplemented by the Federal Facilities Compliance Act (FFCA), which waived the sovereign immunity of Federal agencies for environmental enforcement actions. The FFCA augmented the power of EPA and State regulators by permitting both to seek injunctive relief, civil penalties and other sanctions against Federal agencies, as well as to criminally prosecute Federal officials.
This new leverage, under CERCLA and later FFCA, to compel cleanup contributed greatly to the development of a cleanup effort commensurate with the range and number of environmental problems for which Federal agencies are responsible. Aggressive early efforts to develop IAGS, however, meant that many cleanup commitments were negotiated without adequate information about site conditions and cleanup requirements, and before sites had been assessed, cleanup approaches and requirements selected, future land use decided, technological feasibility evaluated, or the relative priorities across different sites and facilities compared. Consequently, performance milestones set by the IAGs often proved unachievable. These milestones also assumed that funding levels would be sufficient to meet projected cleanup requirements on an ambitious schedule. The schedules did not anticipate funding constraints inherent in the budget process. Thus, the IAGs and the budget process at times established potentially conflicting sets of mandates and requirements, all of which may be enforced by Federal and State regulators with the threat of injunctive relief, civil penalties, and criminal sanctions against Federal officials.
D. Renewing the Commitment to Cleanup.
The Clinton Administration is fully committed to safeguarding human health, safety, and the environment at Federal facilities and surrounding communities, and to complying with requirements of the environmental laws. Further, the Administration acknowledges that existing problems require prompt and efficient restoration and cleanup. In order to ensure that public funds are used as efficiently as possible in meeting this obligation, the Administration must implement statutory, regulatory, administrative, and managerial changes that will speed the cleanup process -- making it faster, fairer, more efficient, and more responsive to local communities.
III. Owning up to the Federal Responsibility.
A. Survey of Agency Challenges.
The nature and type of sites across agencies where environmental cleanup or restoration is required vary, but these sites can generally be grouped into three major categories: the nuclear weapons complex; non-nuclear industrial contamination sites resulting from Federal operations; and, land managed by Federal agencies with contamination from governmental or private activities.
The first category of sites, the nuclear weapons complex, is comprised of facilities that developed, produced, and tested nuclear weapons. These sites are owned and operated by the Department of Energy (DOE) and represent the most complex, and potentially the most expensive, remediation challenges. The sites contain radiological and mixed (radiological/chemical/ hazardous) wastes that present unique technological and practical impediments to prompt remediation and restoration.
The second category is comprised of those sites where Federal operations have generated environmental problems similar to those found in the private sector. For example, the releases of hazardous substances associated with solvents and fuels from vehicle or airport operations at DOD or National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) facilities are comparable to those found at similar operations in the private sector. The industrial contamination sites in this category, while the most numerous, are the sites for which knowledge about risk and remedial technology is most developed and understood.
The third category of sites are on lands administered by Federal agencies, at which either governmental or private parties have disposed of hazardous substances or are otherwise responsible for contamination. Contamination at these sites has a range of causes: from hazardous substances leaching from disposal areas to release from mining and milling operations left by private parties on lands managed by the Department of the Interior (DOI) and the Department of Agriculture (USDA) Forest Service. Because many of these sites are geographically isolated, or have contamination attributable to non-agency activities, the identification and assessment of these sites is in the earliest stages.
B. Building knowledge about relative risk at sites.
There has been increasing progress in developing our understanding of risk at Federal facility sites and improving the risk-assessment protocols by which cleanup decisions are made. The collective level of knowledge and experience in the use of risk assessment and analysis continues to build, and the science of risk assessment continues to evolve and be refined. Ongoing efforts within the last 18 months by the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), EPA, DOD, DOE, and an interagency working group of Federal agencies have produced new guidelines on risk assessment and priority-setting pertinent to environmental cleanup. These guidelines for assessing risk and tools for comparing risks across sites should strengthen decisionmaking and better ensure that funds are divided first to the highest priority sites.
While the science of risk assessment has been advancing, so too has site-specific progress by each of the responsible Federal agencies. The magnitude and complexity of the problems are unquestionably greatest at DOE. DOD, with thousands of industrial type sites, and NASA, with a limited number of industrial-type facilities, are the furthest along in assessing and addressing identified problems at their sites. USDA and DOI, while making progress in many areas, are by contrast, at the early stages of identifying and responding to their problems at sites with contamination caused by private parties, such as mining operations.
C. DOD: A Relative Risk Framework and Community Partnerships.
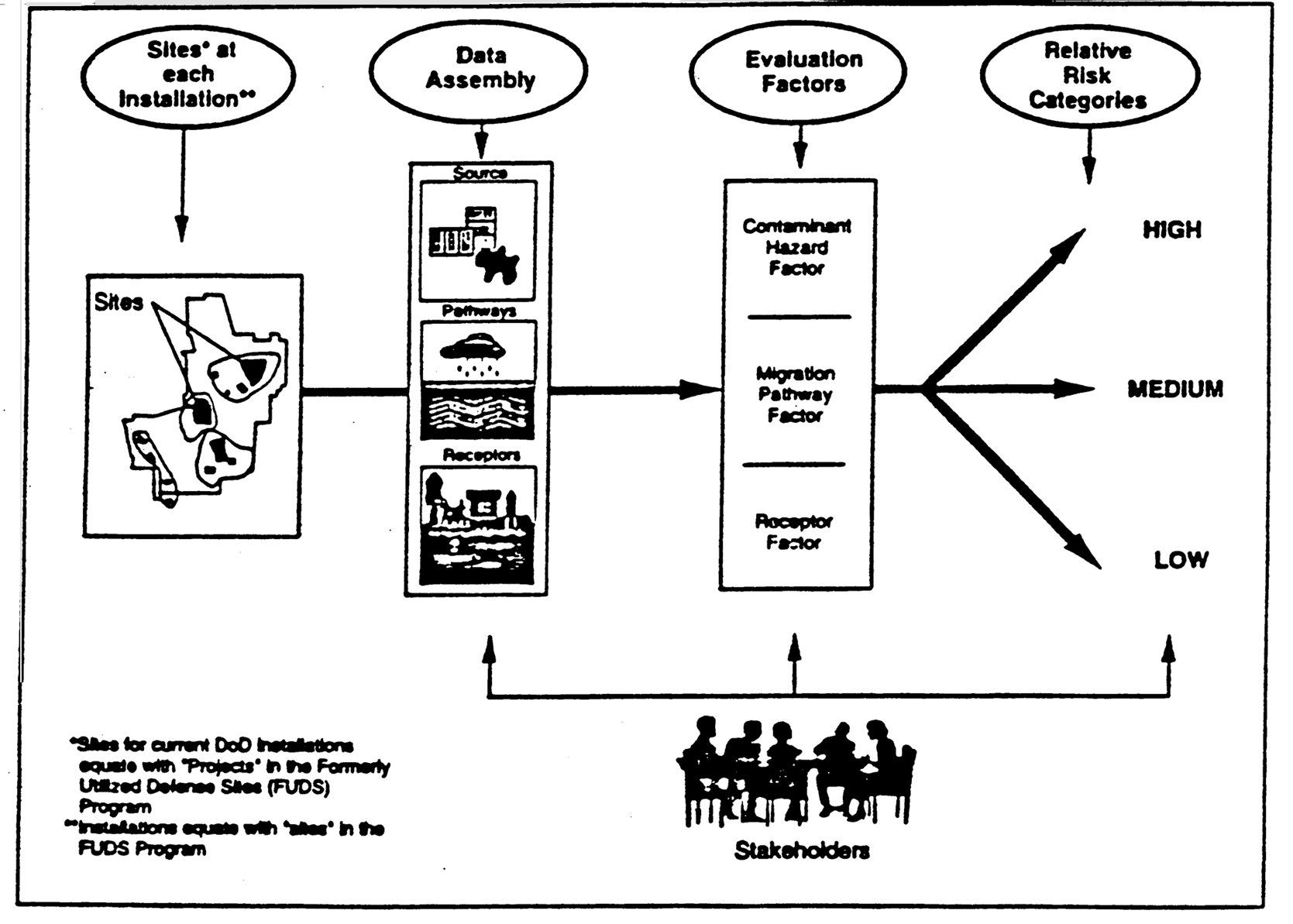
DOD is making significant progress in its cleanup program. However, since the inception of a dedicated funding source in 1984 by Congress, the Department has been unable to document risk reduction or meaningful progress attributable to its cleanup program. As a result, in late 1994, DOD implemented a relative risk framework in order to evaluate its progress in reducing threats to human health and the environment at its sites. Use of this framework as a management and decisionmaking tool, in combination with community outreach, promises significant program improvement.
Under the framework, sites are grouped into low, medium, or high relative risk categories. In making these judgments, DOD first considers the nature of the contaminant, the pathway (i.e. likelihood of transport of contaminants by soil, groundwater, or surface water), and the possible receptors (portions of the public or environment that may be biologically affected). The results of this analysis are presented to Restoration Advisory Boards (RABS) at installations for their review and discussion.
In designing the relative risk framework, DOD incorporated early stakeholder involvement by using RABs as a mechanism for discussing the relative risk ranking of sites at installations. RABs serve as a forum for exchanging cleanup information with concerned Federal and state officials and local stakeholders. The Department's plan is to expand the number of RABs that participate in the relative risk ranking of sites at DOD installations. RAB members are able to advise and provide input that may change the final ranking of a site at an installation. The involvement of RABs in the relative risk framework has helped to open an earnest dialogue and partnering between stakeholders and the Department at the local level. As a result, DOD has had considerable success when RABs have participated in relative risk ranking of sites at its installations.
In recent years, DOD has increasingly focused its cleanup funding strategy on efforts required by schedules and milestones in agreements in order to meet the Department's overall budget targets. This funding strategy resulted in more sites being covered under agreements, since it was the only mechanism to obtain funding. However, the Department's approach did not always ensure funding was allocated to the most urgent sites. Beginning in FY 1996, DOD began the transition to a budget based on reducing relative risk while still meeting all legal agreements. In FY 1997, the Department will base its budget on reducing relative risk at sites while meeting schedules and milestones in legal agreements. Furthermore, the Department will work with the regulatory community to stretch cleanup schedules at sites with lower relative risk until funding becomes available.
D. DOE: Ongoing Process Improvements.
DOE is now implementing fundamental reforms in its programs and improving the performance of its environmental management and restoration activities. DOE has undertaken a major contract reform initiative to provide contractors more incentive to improve performance and contain costs. DOE has increased the number of staff devoted to contractor oversight and cost-estimation; it has made much greater efforts to identify and adopt best practices from industry and to share knowledge across sites; it has pressed for contract reforms to improve efficiency among its contractors; and it has accelerated efforts to explore innovative cost-savings measures, such as privatizing the remediation of tanks containing liquid radioactive waste by competitively contracting out on the basis of fixed unit price for treated waste. DOE has created Site-Specific Advisory Boards (SSABs) to increase local stakeholder knowledge of, and participation in, the cleanup process. Discussions with the advisory boards include the formulation of strategies based on reasonably anticipated future land use. Additionally, DOE has just completed its first comprehensive assessment of program costs and risks across the DOE complex which has more closely tied priorities to risk and cost factors.
IV. Paying the Cold War Mortgage: Remaining Challenges.
A. The Potential Funding Gap.
The Federal government is spending about $9 billion a year to address the cleanup problem, including DOE's ongoing waste management. As the table below shows, there is much work to be done. The total outstanding cost is estimated to range from $234 billion to $389 billion over the next 75 years. The range provided is broad mostly because of uncertainties
|
Total Estimated Cost to Complete Cleanup by Agency |
|
Department of Energy |
$200-$350 |
|
Department of Defense |
$26 |
|
Department of the Interior |
$4-8 |
|
U.S. Department of Agriculture |
$2.5 |
|
National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
$1.5-2 |
|
Total |
$234 to $389 |
in DOE's future costs. Total cost estimates are likely to change over time as knowledge and experience improves. However, the sheer magnitude of the projected costs in relation to the annual total discretionary Federal budget (about $550 billion annually) underscores the imperative to set priorities in allocating Federal cleanup resources wisely and efficiently.
Balancing budgetary objectives is particularly constraining for DOE, in light of the obligation to meet the requirements of over 70 active compliance agreements entered into with EPA and various States. In the next five years, DOE will face the most significant challenge of any agency in being able to stay within budget targets established by the Administration. In fact, as this report shows, budget targets in the next five years will require major additional changes to the way DOE does business. The EM program plans to achieve significant progress in streamlining the DOE contractor work force, reducing indirect and overhead labor costs, and contract reform; but these may be an insufficient source of savings to stay within the prescribed resource levels.
In DOD's case, reduced appropriations for the Defense Environmental Restoration Account (DERA) during the past three fiscal years have led to renegotiations of milestones with regulators. DOE has also begun the process of reevaluating and, where necessary, renegotiating cleanup agreements to incorporate greater sensitivity to cost, risk, and technological feasibility.
B. The Need for Statutory and Regulatory Reform
Federal facility cleanups are currently governed primarily by CERCLA, the corrective action requirements of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), the Atomic Energy Act (AEA), and State laws. The CERCLA process of remedy selection includes a preference for permanence and treatment in remedies and also may use applicable and relevant or appropriate requirements (ARARS) of Federal and State laws. Many of these factors generate uncertainty concerning appropriate cleanup levels and significant in costs that may be unwarranted at many sites. Further complicating the process is the potential overlay of one authority on another, as where a state asserts its RCRA authority to impose additional requirements at a CERCLA site, or where a site currently being addressed under RCRA is proposed for listing on the National Priority List (NPL) under CERCLA. The complex interweaving of requirements needs statutory, regulatory, and administrative simplification and reform to permit more rational priority-setting according to risk, appropriate consideration of costs and benefits, and remedial action tied to anticipated future land use.
C. The Special Problem of Radioactive Waste.
Radioactive waste presents a great remediation challenge for the Federal government. Much of this waste will remain radioactive for many years -- up to tens of thousands of years. It cannot generally be neutralized, but must be contained instead. In many cases, treatment technology is not available. Because of the potential impact upon future generations, remediation plans must essentially provide for perpetual care of long-lived wastes and take into account unusual technical concerns of residual radionuclides. Even characterization of the waste has been difficult due to the health risks to workers. A lack of agreement upon the threshold levels in soil, surface or groundwater that will prevent unacceptable risks to human health, as well as related uncertainties about future land use of former weapons production sites, pose major obstacles to DOE's efforts to conduct remediation at these sites. As DOE has pointed out in its recent Baseline Environmental Management Report (BEMR), decisions regarding land use. in particular, as well as allowable residual contamination and technology advances, will dramatically affect the cost; and, given limited resources available, the timetable for remediation.
This survey of the current state of the Federal facilities cleanup efforts identifies an agenda for reform in five areas, all of which are essential to enhancing the cleanup effort, improving efficiency in the deployment and use of available resources, and maintaining public acceptance and credibility. These areas are 1) statutory reform, 2) administrative and regulatory reform, 3) management reform, 4) cost-effective technology development and implementation, and 5) budget process reform.
A. Principles of Reform.
The efforts to address the many significant problems confronting Federal facility cleanup must be undertaken within a framework of principles that guide, inform, and constrain whatever reforms are needed to improve the efficiency and credibility of the cleanup effort. Extensive and productive discussion among Federal agencies, States, communities, and others have identified a number of the principles that should govern Federal facilities cleanups, and these are equally important to the reform effort. After a process of review and synthesis, the FFPG has endorsed a set of principles each of which is drawn from sets of principles drafted by either the Environmental Commissioners of States (ECOS) or the Federal Facilities Environmental Restoration Dialogue Committee (FFERDC). The topics covered include:
State role;
Federal role;
Independent State regulatory oversight;
Negotiated compliance agreements;
Efficiency;
Long-term commitments;
Equity;
Integrated planning and response;
Public participation;
Environmental justice;
Pollution prevention and pollution control activities;
Reasonably anticipated future land uses;
Cleanup contracting;
Human health risk in decisionmaking;
Systematic decisionmaking and priority setting; and
The role of studies in cleanup.
B. Statutory Reform.
In the 103rd Congress, the Clinton Administration developed a comprehensive set of reforms to CERCLA that had broad bipartisan support and hewed closely to the principles just described. The Administration's bill, H.R. 3800, attracted the support of a broad coalition of groups concerned about the Superfund program, ranging from environmental and community groups to States and industry. Despite this support, legislation reauthorizing the Superfund program was not passed. While the current Congress has not yet developed any proposals with similarly broad support, the Administration will continue to advocate responsible reforms to CERCLA and to support statutory changes that conform to the principles recited here and reflected in last year's bill.
As part of a broader National Performance Review process of "Reinventing Environmental Regulation," the Administration announced in mid-March 1995 that it would convene a series of stakeholder discussions intended to develop a narrow set of targeted reforms to RCRA that would eliminate or modify requirements that generate high costs and only marginal environmental benefit. [ "Reinventing Environmental Regulation, " Environmental Protection Agency (Washington, D.C.: March 16, 1995).] As in the case of CERCLA, any proposed reforms would apply equally to responsible parties in the public and private sector, but the reforms discussed in the stakeholder process would provide significant relief to Federal facilities.
C. Administrative and Regulatory Reform.
Soon after the 103rd Congress adjourned without enacting a Superfund reform bill, EPA announced a series of reforms to begin implementing as many of the proposals in the Administration's bill as current law permits. Where appropriate, EPA has sought corresponding reforms to RCRA. Reforms include:
linking future land use with remedy selection;
increasing consideration of cost and risk issues in remedial decisions;
streamlining standards and reducing redundancy through RCRA/CERCLA integration guidance;
increasing use of risk-based priority setting among Federal agencies
revising milestones in IAGs to reflect priority setting; and
promoting economic development.
D. Management Reform.
DOE has budgeted 20 percent in management savings to be realized through efficiency gains, in addition to the already substantial gains that have been achieved by eliminating historic inefficiencies. Further and dramatic reforms in the areas of contracting methods and management, and the internal management of the agency, are necessary. Some of these initiatives may prove useful for cleanup programs in other departments. Other management initiatives that would improve the cleanup process include: improving information systems to help managers do better strategic planning, budgeting and oversight; improving strategic planning and oversight at agency headquarters; and moving to privatize whenever cost-effective.
E. Cost-Effective Technology Development and Implementation.
F. Budget Process Reform.
As Federal resources to meet all national needs become more constrained, public awareness of the important contribution made by the Federal budget process in setting priorities for Federal facilities cleanup and in governing the pace of their accomplishment has grown. Along with self-imposed mandates for continuing program improvement, national fiscal conditions are forcing agencies to prioritize their cleanup efforts within and across sites according to better evaluation of alternative future land uses, estimates of risk, evaluations of available technologies, and analyses of the relative costs and benefits of alternative approaches to cleanup. Negotiated cleanup agreements should continue to play an important role in the Federal agency cleanup program, but more flexible agreement structures are needed to help ensure that limited resources are used as wisely as possible. In order to ensure that the limited Federal resources available to protect public health and safety and the environment are used as wisely as possible, agreements should recognize the need to address the most urgent risks first, incorporate these more rigorous methods of establishing cleanup priorities, and be capable of ready adaptation to new information, budget constraints, and changing circumstances. These kinds of negotiations will obviously be difficult, but they are critical if the Nation is to come to grips with the dilemma posed by limited resources and the extraordinary costs of addressing this problem.
In addition, the Federal budget process should continue to pressure agencies to implement management reforms that will reduce costs of operations. For example, cost savings include: speeding the adoption of cost-saving technologies, using more cost-effective contracting methods, adopting best practices for other agencies and the private sector, streamlining management structures and processes, and eliminating unnecessary overhead. Systematic introduction and evaluation of performance measures in the budget process can facilitate accomplishment of this goal.
More stable funding of Federal agency cleanup programs can help ensure that cost-effective programs focused on risk reduction are implemented. When funding levels vary widely from year to year, Federal agencies cannot conduct efficient efforts that maximize the taxpayer’s returns on investment. Finally, if the process is to work, all stakeholders must be informed about and have meaningful opportunity for input into key decision-making processes.
VI. Conclusion
The Federal government is making progress and improvement in the environmental cleanup and restoration at Federal facilities. However, further improvement in the efficiency and effectiveness of cleanup programs is necessary, if we are to meet public expectations for adequate safeguarding of human health and the environment, and environmental cleanup of Federal facilities and Federally administered lands. Continued vigorous implementation of management reforms, development of an innovative technologies strategy, statutory, administrative and regulatory changes, as well as stabilized funding, will all be necessary if we are to accomplish this goal within strained resources. Federal facility restoration cannot be accomplished by the Federal government working alone. Continued productive collaboration among all stakeholders is essential for long-term success.
I. Introduction.
The environmental cleanup of Federal lands and facilities would pose enormous scientific, technical, administrative, regulatory, and political challenges, even if resources available for this purpose were unlimited. As the Federal government works to reduce spending to eliminate the Federal budget deficit, all Federal programs must compete for a shrinking pool of discretionary resources. This reduction in resources requires concerted action to maximize the net benefits achieved from every dollar invested in Federal facilities cleanup. There is general consensus that this objective requires far more rigorous risk-based priority setting and management improvement, both within and across sites, than have been achieved to date, as well as statutory and regulatory reforms to remove impediments to success. The ability of policy makers, program managers, regulators and other stakeholders collectively to define and carry out specific reforms will determine whether the Nation's multi-billion dollar investment in Federal facilities cleanup succeeds or fails.
This report presents the analysis, conclusions, and recommendations of the Federal Facilities Policy Group (FFPG), convened by the Director of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the Chair of the Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) to review the current status and future course of environmental response and restoration at Federal facilities. [The Federal Facilities Policy Group is co-chaired by Alice M. Rivlin, Director of the Office of Management and Budget, and Kathleen McGinty, Chair of the Council on Environmental Quality. The Policy Group is composed of policy officials from the Departments of Agriculture, Defense, Energy, Health and Human Services (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry), the Interior, and Justice, along with the Environmental Protection Agency, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. In addition, several White House offices, including the President's Council of Economic Advisers, the Domestic Policy Council, the National Economic Council, and the Office of Science and Technology Policy have participated.] Specifically, this report identifies areas of management and regulatory reform essential to protect public health and restore the environment, as well as to assure effective, efficient use of resources as the effort to clean-up Federal facilities proceeds.
II. Origin of the Problem.
Over the last 25 years, public awareness of the human health and environmental hazards associated with the release of toxic, hazardous, and radiological substances has grown dramatically. The worst hazardous waste problems, such as the Love Canal site in New York, focused public attention on the lack of adequate Federal regulation and resources to guard against the future release of hazardous substances or to address cleanup of sites already contaminated. From the late 1970s onward, these concerns generated an array of Federal responses designed to hold responsible parties accountable for the proper handling and disposal of hazardous materials, while also providing for the cleanup of existing contamination.
Lack of sensitivity to environmental protection by some agencies was also a problem on Federal lands and at Federal facilities around the country. For some agencies, the sense of urgency to develop a stockpile of nuclear weapons and maintain a prepared military force during the Cold War, coupled with the secrecy and compartmentalization of information required for nuclear technology security, resulted in long delays before significant environmental problems were understood or addressed. Consequently, the extent of existing contamination on Federal lands is only now being fully characterized and the enormity of the cleanup challenge adequately recognized.
Initial studies conducted at Federal agencies document the enormous challenge presented by Federal facilities contaminated with radioactive or hazardous waste. Much of the radioactive waste is a by-product of the Department of Energy's (DOE) nuclear weapons research, production and testing. The Department of Defense's (DOD) operations have also generated hazardous waste contamination similar to that found in the industrial and commercial sectors. Thousands of abandoned mines and other contaminated sites are found on public land managed by the Department of the Interior (DOI) and the Department of Agriculture (USDA). Chemical and radiological substances at Federal facilities have contaminated air, topsoil, sediments, surface water, and groundwater, as well as vegetation and wildlife, thereby posing significant threats to human health and safety and the environment.
Federal leadership in meeting the cleanup challenge and making appropriate cleanup decisions for the diverse portfolio of sites under Federal management is a legal and economic imperative. Some of these hazardous waste sites present a risk to public health and the environment for communities serving as hosts to essential government missions, such as weapons production and some defense operations. The Clinton Administration recognizes a moral commitment to these communities, and to current and future generations, to address the risks posed by hazardous substances at these facilities. Successive Congresses have translated this imperative into a legal mandate, reflected in a host of specific environmental compliance obligations imposed by statute on Federal agencies. The economic significance of these obligations is increasing, because efficient and effective cleanup decisions at these facilities are necessary to meet targets for reduced Federal spending and to facilitate the environmental and economic redevelopment and beneficial reuse of Federal facilities. This is especially important as the closure of DOD bases and the overall reduction in the number of Federal facilities renders large numbers of facilities available for economic redevelopment or transfer to other Federal uses.
Although there is consensus on the obligation to address contamination at Federal facility sites, there is insufficient agreement on the scope of the obligation or the appropriate standards to guide decisions about remediation, restoration, and future use of Federal agency sites. Indeed, the magnitude of the challenges presented by the commitment to address the numerous, diverse, and complex environmental problems at Federal facilities underscores the importance of making the best possible judgments concerning risk, priority, cost, and cleanup levels. Yet, even as our knowledge about sites has improved, there remains considerable debate and little consensus concerning the precise nature and severity of risks presented at certain Federal facility sites, the standards that should apply in determining cleanup levels, the priority and pace of cleaning up the portfolios of sites managed by each agency, and the role of costs and benefits in developing and constraining cleanup strategies.
The 1980s, the first full decade of effort by Federal agencies to address contamination at their facilities, yielded little actual cleanup until the end of the decade. The Cold War secrecy that shrouded a number of Federal facilities hindered rapid assessment of the environmental conditions at those sites. At some agencies, environmental protection and restoration were not typically given priority among other competing agency missions. Further, the lack of a separate environmental function and expertise within agencies, or of a clear mandate for environmental awareness in the performance of mission activities, hampered commitment and effort during these years. Some agencies bridged this gap with a heavy reliance on contractors, at times with losses in accountability and failure to control costs.
These difficulties were compounded by very real limitations on public knowledge, technology, and communication -- a number of which still exist today. At the inception of their remedial programs in the early 1980s, agencies knew little about the extent and nature of their contamination problems or about the relative risks and priorities among sites. Agencies had not set priorities or allocated resources as necessary to investigate or assess the contamination at their sites. Cleanup technologies often were unavailable, and, in important instances, are still in early stages of development. Some agencies also had little experience in communicating effectively with local communities and other stakeholders due to their long history of secrecy at many sites. These communication difficulties contributed to further public distrust of operations at those Federal facilities and to a lack of public confidence in the Federal commitment to eventual cleanup of Federal lands.
The Lack of Knowledge: During the early years of Federal facility cleanup, knowledge limitations significantly impeded cleanup progress. Initially, little was known about the extent or range of the potential sources of existing contamination. To tackle this challenge, agencies had to first characterize each site, a process which involved testing to determine the presence, type, quantity, and location of contaminants; subsequent evaluation of how those contaminants move and change after entering the environment; and finally, a prediction of the direction and rate of contaminant migration. Characterization has proven to be time-consuming, costly, technically difficult, and fraught with uncertainty, but it is essential for sound risk assessment and effective, efficient cleanup decisions. [Office of Technology Assessment (OTA), Complex Cleanup; The Environmental Legacy of Nuclear Weapons Production , OTA-0-484 (Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, February 1991), pp. 32-39.] At large, complex facilities like those of DOE, comprehensive, integrated assessments have been especially difficult to accomplish. Moreover, just determining how far to pursue characterization at a particular facility or site has not been easy. The value of additional information has had to be weighed against its real costs, including delay in moving to cleanup and diversion of resources away from cleanup.
Agencies often have had to undertake these tasks without fundamental scientific knowledge of certain contaminants or combinations of contaminants. Such knowledge, however, remains essential to the development of sound, science-based. protective standards for the off-site public, for on-site workers, and for the environment. Knowledge regarding the effects of hazardous and toxic substances and materials on human health and other biological receptors has been and remains incomplete. Specifically, a greater scientific understanding about the toxicity, health effects, and interaction of environmental contaminants known to exist at Federal facilities is needed. [Ibid.; OTA, Hazards Ahead: Managing Cleanup Worker Health and Safety at the Nuclear Weapons Complex (Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, February 1993); Portney, Paul, "EPA and the Evolution of Federal Regulation " in Dorfman, Robert and Dorfman, Nancy S. (ed.), Economics of the Environment: Selected Readings (Third Edition) (New York: W.W. Norton, 1993), p. 72; Science Advisory Board, Reducing Risk: Setting Priorities and Strategies for Environmental Protection (Washington, D.C.: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 1990), pp. 8, 18.] For example, sediments in lakes and streams surrounding DOE's Oak Ridge Reservation contain both radionuclides and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). The biological consequences of such multiple exposures may be very different from the effects of individual contaminants. Once inside an organism, environmental contaminants can accumulate, interact by impinging on the same organ system, or alter the metabolism of other contaminants. [OTA, Complex Cleanup, p. 94.] The need for more complete information on the biological impact of environmental contaminants is well-documented, [National Research Council, A Biological Survey for the Nation (Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press, 1993), p. 95.] yet answers to some of these questions may be unavailable for years.
A Lack of Cost-Effective Technology: During much of the history of Federal facilities cleanup, effective and proven technologies for certain cleanups have not existed, and the cost of others has been prohibitive. This has been particularly true for DOE radioactive waste cleanup. [Congressional Budget Office, Cleaning Up the Department of Energy's Nuclear Weapons Complex (Washington, D.C.: U S. Government Printing Office, May 1994), pp. 35-50; OTA, Coomplex Cleanup , pp. 67-71 and 168-182.] Even characterization technologies, which are used to determine the types of contaminants present at many sites, have frequently been either ineffective or too costly. [U.S. Department of Energy, Estimating the Cold War Mortgage: The 1995 Baseline Environmental Management Report, DOE/EM-032 (Springfield, VA: National Technical Information Service, March 1995), p.6] Still, new technologies often present the best hope for ensuring a real reduction in risk to the environment and improved worker and public safety. DOE has identified five such areas where new technological solutions are most needed to facilitate cleanup: ground water contamination; plutonium in soil; silos with uranium processing residues; single-shell, high-level waste tanks; and buried transuranic waste. In addition, improvements in material removal, handling and processing technologies are needed to enhance safety and reduce costs. Federal agencies have encouraged the development of promising technologies, but some will not be available for many years. Consequently, the Federal government’s ability to accurately gauge the cleanup cost, timetable, and associated risks has been significantly limited in the past and even today is uncertain.
The Problem of Federal/Public Communication: The public demand for information on existing contamination and for involvement in decisions addressing these problems has significantly increased. Until the past few years, however, the role of locally affected populations in cleanup decisions was extremely limited. The remoteness of certain Federal facilities, the secrecy surrounding national security activities, and management cultures oriented toward other missions all contributed to the absence of systematic efforts to address the concerns and interests of local stakeholders. Secrecy that was once critical for the security mission at some agencies persisted long after agency missions had changed, which impeded public involvement and undermined public confidence.
2. Early Responses.
This new leverage, under CERCLA and later the FFCA, to compel cleanup contributed greatly to the development of a cleanup effort commensurate with the range and number of environmental problems for which Federal agencies are responsible. Aggressive early efforts to develop IAGS, however, meant that many cleanup commitments were negotiated without adequate information about site conditions and cleanup requirements, and before sites had been assessed, cleanup approaches and requirements selected, future land use decided, technological feasibility evaluated, or the relative priorities across different sites and facilities compared. Consequently, performance milestones set by the IAGs often proved unachievable. These milestones also assumed that funding levels would be sufficient to meet projected cleanup requirements on an ambitious schedule. The schedules did not anticipate funding constraints inherent in the budget process. Thus, the IAGs and the budget process at times established potentially conflicting sets of mandates and requirements, all of which may be enforced by Federal and State regulators with the threat of injunctive relief, civil penalties, and criminal sanctions against Federal officials.
These early difficulties, however, do not warrant a turning away from our Federal responsibilities. The Federal government has a legally-recognized obligation to clean up the legacy of environmental contamination caused by Federal operations across the United States.
1. The Administration Commitment.
The Clinton Administration is fully committed to safeguarding human health, safety, and the environment at Federal facilities and surrounding communities, and to complying with requirements of the environmental laws. Further, the Administration acknowledges that existing problems require prompt and efficient restoration and cleanup. In order to ensure that public funds are used as efficiently as possible in meeting this obligation, the Administration must implement the statutory, regulatory, administrative, and managerial changes that will speed the cleanup process -- making it faster, fairer, more efficient, and more responsive to local communities.
The basic goal of environmental cleanup efforts at Federal facilities is to protect human health (of both workers and the public) and the environment by reducing the risks caused by past and present activities at those facilities. In principle, there is wide agreement with this statement among Federal officials and other concerned parties who have sought compliance by Federal agencies with applicable environmental laws. In practice, there is substantial disagreement concerning the priorities and standards that should govern the cleanup effort.
These basic goals have not yet been attained, because, as has been found true for hazardous waste cleanup in the private sector, cleaning up Federal facilities has proven to be a larger, more complex, and more expensive challenge than most people first envisioned. These issues have been the focus of intense scrutiny at a time of widespread public distrust of government and mounting pressures to reduce government spending. This requires Federal agencies responsible for hazardous waste cleanup to refine their strategies for attaining the basic goal and adopt attainment strategies that reflect current resource and knowledge constraints. These strategies must set priorities and allocate resources in a manner and through a process that leads to greater efficiency and greater public acceptance. The process must recognize that the pace and level of cleanup depend upon appropriations from Congress and that there will be diminishing fiscal flexibility. Accordingly, the development and implementation of these strategies must ensure better use of existing funds. The process must foster more cost-effective cleanup choices, greater attention to cost, better management, and decisional criteria to ensure that the benefits of particular cleanup choices justify costs.
At the same time, we must recognize that each agency has made significant commitments to the communities in which they are located. Any processes for priority-setting and revising cleanup decisions or timetables must be transparent, with substantial opportunities for meaningful participation by affected communities. These processes must take into account other significant Federal policies relevant to environmental protection, including those promoting economic growth, beneficial reuse of closing Federal facilities, and environmental justice.
III. Owning Up to the Federal Responsibility.
Federal government activities have caused a variety of environmental impacts. The nature and type of sites where environmental cleanup or restoration is required vary, but these sites can generally be grouped into three major categories: the nuclear weapons complex, non-nuclear industrial contamination sites resulting from Federal operations, and land managed by Federal agencies with contamination from private activities.
The first category of sites, the nuclear weapons complex, is comprised of facilities that developed, produced, and tested nuclear weapons. These sites are owned and operated by DOE and represent the most complex, and potentially the most expensive, remediation challenges. Long shielded from regulatory oversight, they contain radiological and mixed (radiological/chemical/hazardous) wastes that present unique technological and practical impediments to prompt remediation and restoration.
The second category is comprised of those sites where Federal operations have generated environmental problems similar to those found in the private sector. For example, the releases of hazardous substances associated with solvents and fuels from vehicle or airport operations at DOD and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) facilities are comparable to those found at similar operations in the private sector. Only ordnance disposal areas, a very small percentage of DOD contamination, represent a unique cleanup challenge. The industrial contamination sites in this category, while the most numerous, are consequently the sites for which knowledge about risk and remedial technology is the most developed and understood.
The third category of sites are on lands administered by Federal agencies, at which either governmental or private parties have disposed of hazardous substances or are otherwise responsible for contamination. Contamination at these sites has a range of causes, from hazardous substances leaching from disposal areas to releases from mining and milling operations left by private parties on lands managed by the Department of Interior and the USDA Forest Service. Because many of these sites are geographically isolated or have contamination attributable to non-agency activities, the identification and assessment of these sites is in the earliest stages. The Federal Facilities Profile table on page 17 summarizes the scope of the cleanup challenges faced by each agency.
The contamination within DOE's nuclear weapons complex, a legacy of 50 years of nuclear weapons production, presents the most difficult challenge, because much of the waste -- almost one million cubic meters -- is radioactive and currently cannot be eliminated or even neutralized. It must be contained, stabilized, or moved to a safer place until treatment and disposal technologies or facilities are available. Certain radioactive materials will require tens of thousands of years to decay naturally. Remediation plans and other risk reduction measures for much of DOE's waste therefore pose unusual technical concerns and require essentially perpetual care of radioactive waste with long half-lives.
DOE now must manage a large inventory of stored wastes and clean up contamination at 137 DOE facilities in 33 States and one territory. This represents over 1,200 separate cleanup tasks -- with over 10,000 potential release sites -- that are known throughout the complex today. The most pressing cleanup challenge consists of 15 major facilities and a dozen or so smaller facilities. Six of the major facilities -- Hanford, Savannah River, Oak Ridge, Fernald, Idaho National Engineering, Laboratory and Rocky Flats -- account for approximately 80 percent of DOE's environmental management budget. In addition, DOE is responsible for environmental cleanup at other facilities formerly used in the production of weapons or the mining and enrichment of uranium and for cleaning up mixtures of radioactive and hazardous waste. Contamination at these sites is primarily comprised of radioactive and hazardous wastes and fissile material. These contaminants present technological cleanup challenges unique to DOE. The most common contaminated areas are buildings, soil, storage tanks and basins used in the past for waste disposal.
DOE's Environmental Management (EM) program has four major responsibilities:
Environmental restoration activities at more than 10,000 potential release sites (grouped into 850 subprojects) to characterize the extent and nature of contamination and potential risks, remove and/or stabilize contaminant sources, remediate contaminated media, decontaminate and decommission surplus facilities, and monitor facilities after closure
Technology development programs to expedite and support remediation and waste management activities; and
Nuclear materials and facilities stabilization activities to manage approximately 2,600 contaminated surplus facilities that have been transferred to EM from other DOE programs and that may require deactivation, stabilization, surveillance, and maintenance.
Thus, the EM program consists of both managing existing and newly generated wastes and cleaning, up historic contamination. This is significant for two reasons. First, the cleanup programs at all other Federal agencies discussed in this paper -- DOD, NASA, DOI, and USDA -- do not include management of existing wastes in their scope or cost estimates. Second, the nature of the laws for day-to-day management differ from those for cleanup. Laws governing day-to-day waste management are generally more prescriptive and technical and tend to be focused on preventing or restricting environmental releases at active facilities. Their enforcement is characterized by a near-term focus and strict technical interpretation. Laws governing cleanup, however, generally focus on actual or potential releases of contamination at inactive facilities or where there has already been a release to the environment. Thus, enforcement can be characterized by both an immediate focus on managing existing, newly generated, and future waste and by a longer-term focus on remediation of previously contaminated sites with the potential for greater flexibility in negotiating compliance activities. It is important to distinguish between day-to-day environmental compliance and longer-term cleanup projects to ensure that in the debate over the setting of priorities, those pollution-avoidance activities that serve as the backbone of our Nation's environmental program are not inadvertently compromised.
The life-cycle cost estimates of the various aspects of EM's activities outlined above are detailed in the March 1995 report released by DOE entitled The 1995 Baseline Environmental Management Report (BEMR). [U.S. Department of Energy, Estimating the Cold War Mortgage, p. 5.] The report represents the DOE's most comprehensive effort to date to estimate the scope and cost of its environmental responsibilities. The total cost estimate ranges from $200-$350 billion, in constant 1995 dollars, over a 75 year period from 1995-2070. Five major sites (Hanford, Savannah River, Rocky Flats, Oak Ridge, Idaho) represent 70 percent of the total estimate, and 90 percent of these costs would be incurred by 2035.
The Base Case presented in the BEMR incorporates a broad range of site-specific assumptions for future land use, cleanup levels, and technology, as well as the pace, priority, and configuration of activities. The assumptions in the BEMR report, which have a major impact on the estimates presented, include the following:
The BEMR estimates exclude projects for which no current feasible remediation approach exists, such as: nuclear explosion test areas (e.g. the Nevada Test Site); large contaminated river systems, like the Clinch, Columbia, and Savannah rivers; most groundwater (even with treatment, future use will remain restricted)- and some special nuclear materials (e.g. 50 tons of plutonium not now identified as surplus). Long-term surveillance and maintenance costs of $50-$75 million per year are also excluded.
The low and high ends of the overall range of estimates vary from the Base Case, depending on important assumptions about productivity over the life of the program. The Base Case estimate of $230 billion assumes a highly ambitious 20 percent increase in productivity and efficiency over the next five years and an additional 1 percent annual productivity improvement over the life of the program. The low end figure, $200 billion, assumes a 20 percent increase in productivity over the next five years, followed by a 2 percent annual increase in productivity improvement. The high-end of the range, $350 billion, assumes continuation of current levels of program efficiency.
As DOE's analysis demonstrates, any estimate of the overall cost of DOE cleanup is subject to great uncertainty, and the range of estimates would clearly be much higher if productivity goals were not achieved, less conservative land use patterns were chosen, or remediation activity were required at currently excluded sites.
Currently, DOE divides its Environmental Restoration activities into 17 primary projects (primarily corresponding to the major DOE facilities) and 850 subprojects. [U.S. Department of Energy, Environmental Management 1995-Progress and Plans of the Environmental Management Program (Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, February 1995), p. 5.] DOE expects that, at the end of 1994, characterization of 33 percent (282) of its subprojects was complete, that an additional 12 percent (100) will be continued, and that 9 percent (78) will be completed in 1995. More is beginning to be spent on actual remediation work than on assessment and characterization. Fifty-six percent of total environmental restoration funding of $1.8 billion in FY 1995 is directed toward remediation, or deactivation and decommissioning, with 44 percent going to assessment. In FY 1994, the split was 50/50.
It is more difficult to establish meaningful overall performance measures for the waste management, technology development, and nuclear materials and facility stabilization program areas. Current measures tend to be project specific. For example, DOE sought a 2 to 4 million gallon reduction in leakage from tanks at Hanford and a 2.4 million gallon reduction was realized in 1994; waste management processed 19.2 million gallons of liquid waste, close to its goal of 20.2 million gallons; and 23 of 24 tank safety activities were completed at Hanford. While these measures represent progress toward defining results, considerable opportunity exists for integrating and further improving measures to give a truer picture of overall EM performance. DOE also has begun meeting its goal of better allocating its resources according to risk. For example, the Department's draft risk report concludes that 78 percent of DOE's EM budget is devoted to high and medium risk activities.
The terms of DOE's 71 active interagency agreements require DOE to meet a schedule of activities that serve as enforceable milestones. These milestones have played a major role in EM's planning, budgeting and priority setting. About 80 percent of the EM's budget is specifically directed to meet requirements of compliance agreement milestones and environmental regulations. In 1994, DOE met 399 of 437 milestones (87 percent). Within EM, the environmental restoration program is responsible for 69 percent of all EM milestones. Waste management completed 99 percent or 127 of its enforceable agreement milestones, an 11 percent improvement over FY 1993. Nuclear materials and facility stabilization had only three enforceable milestones, all of which were completed. Technology development had no enforceable milestones. [Ibid, p. 94.]
2. Industrial Operations Cleanups.
Both DOD and NASA are responsible for cleaning up sites contaminated from industrial operations, although the magnitude of the cleanup challenge faced by each is very different.
Department of Defense.
DOD faces a significant cleanup challenge. Some work started in the late 1970s and continued in the early 1980s. Since 1984, when a separate cleanup fund was created by Congress, the Department has been engaged in cleanup at 21,425 potentially contaminated sites on 1,769 military installations. In addition, the Department is also involved in cleanup activities at Formerly Used Defense Sites (FUDS). FUDS are properties formerly owned by, leased to, used by, or otherwise under the operational control of DOD. The cleanup program at FUD properties is similar to that at DOD installations. There are a total of 8,316 FUD properties potentially eligible for DOD funding.
The majority of DOD sites are associated with past practices involving the use of fuels and solvents for operation and maintenance of activities at military installations. Spills or leaks occurring as a result of these activities may have affected the immediate surface or subsurface areas around the site. In some cases, a contaminant may have been spread to other areas by stormwater runoff or groundwater movement. Many sites are former treatment, storage, or disposal areas, such as landfills and wastewater treatment facilities. There are a few sites that present unusual challenges for DOD: weapons testing ranges where munitions have been used and unlocated, unexploded ordnance may exist; ordnance disposal areas where munitions were buried many decades ago; fire fighting training areas where fuels and other flammable substances have been burned; and low-level radioactive waste areas at which common aircraft dials and other slightly radioactive instruments have been disposed. [Department of Defense, Defense Environmental Restoration Program: Annual Report to Congress for Fiscal Year 1994 (Washington, D.C..: Department of Defense, March 31, 1995) pg. 63. In addition, many thousands of acres of public lands under the management of DOI and Indian tribes have been used by DOD, State National Guard and militia units for weapons testing, and training and are contaminated by unexploded ordnance.]
At the end of FY 1994, DOD had a total of 21,425 potentially contaminated sites on 1,769 military installations. Of these sites, 9,640 have been closed out, mainly through studies that determined no cleanup was needed. As a result, there are currently about 800 installations with 11,785 sites where a study or cleanup is underway. In addition, there are a total of 8,316 FUD properties potentially eligible for DOD funding. At the end of FY 1994, DOD had closed out or determined no DOD respponsibility at 4,604 of these FUD properties.
The pace of DOD’s progress at those sites is reflected in the fact that it now spends more in actual cleanup work than studies -- over 47 percent of its funding was spent on actual cleanup, compared to 40 percent for studies. The remaining 13 percent was spent on program administration costs. In FY 1995, prior to the $300 million rescission, DOD projected that it would invest over 60 percent of its funding for actual cleanup work in FY 1996.
DOD's current estimate for completing its cleanup program is $26.2 billion in 1994 dollars. [cf. Congressional Budget Office, "CBO Papers: Cleaning Up Defense Installations: Issues and Options," January 1995.] DOD's cost estimate is subject to significant uncertainty and is currently being revised to take advantage of more detailed site-level information. DOD has increased its focus on implementing interim measures -- removal actions and interim remedial actions -- to accelerate reduction of risk to human health and the environment. Interim actions result in the stabilization or removal of contamination sources and thereby reduce or eliminate immediate risks. Interim actions, such as installing fences and providing alternative drinking water supplies, greatly reduce risk by eliminating exposure to contaminants. Other interim actions include source removal, capping, and pumping-and-treating groundwater. [Department of Defense, Defense Environmental Restoration Annual Report to Congress for Fiscal Year 1994, Washington, D.C., p. 9.]
At the end of September 1994, 1,387 interim actions at 1,173 sites had been completed, and another 573 interim actions were underway at 551 sites. The number of interim actions completed and underway at any given time are key indicators of DOD cleanup progress, because interim actions involving waste removal and treatment may satisfy final cleanup requirements. For example, the Air Force took immediate action to stabilize a threat posed to a national wildlife refuge by a 10,000 cubic yard ash pile containing lead on Johnston Atoll in the Pacific. EPA Region 9 wanted timely action to control the contamination. The interim action involved spraying the ash pile with a liquid polymer. In two days, this action stopped contaminants from leaching to a nearby lagoon containing endangered species. [ Ibid, pp. 14-15.]
DOD has not systematically collected data on actual risk reduction attributable to its program. DOD is currently evaluating the relative risk of its sites in order to categorize the threat of existing site conditions as either high, medium, or low. DOD expects to tie future funding levels to the reduction of relative risk of its sites. In addition, performance measures are being established for environmental work at closing bases. This will include categorizing the relative risk of sites on closing installations and measuring the availability of property environmentally suitable for transfer.
National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
NASA faces industrial cleanup challenges similar to those of DOD at a relatively small number of facilities. NASA is responsible for cleaning up approximately 730 potentially contaminated sites at ten major centers and seven smaller ones, and believes that this list is complete. At 155 of these sites, no further action is required or active remediation has been completed. Another 350 are currently undergoing site evaluation and preliminary assessment, and 75 are undergoing active remediation. NASA plans to investigate the remaining 150 sites over the next two years.
NASA produced these hazardous wastes through its research, operations, and maintenance activities. To facilitate meeting Federal, State, and local environmental requirements, NASA uses a decentralized management approach, with policy guidance, priority setting and oversight from a central Environmental Management Office. The central office has delegated responsibility for environmental compliance to its ten center directors.
Contaminants at these sites are primarily fuels, solvents and industrial waste attributable to such problems as leaking underground storage tanks, exposed asbestos and mercury spills. The current NASA estimate for completing cleanup is $1.5-2 billion, in constant 1994 dollars. NASA plans to complete its cleanup program within the next 25 years, with annual funding requirements of $45-55 million to meet its environmental requirements. NASA has obligated over $136 million since 1988 for environmental restoration, compliance, and pollution prevention.
3. Land Manager Oversight of Hazardous Cleanups.
DOI and USDA face cleaning up sites where Federal operations caused environmental contamination. In addition, as managers of Federal lands, these agencies may be forced to pay the costs of cleanup for sites contaminated by other parties where it is not possible to recover costs from the responsible parties.
Department of the Interior.
The DOI is responsible for a large number of potentially contaminated sites on the more than 440 million acres of Federal land that it manages. Much of this remediation challenge is the result of actions by users of Federal lands, including private parties, Indian tribes, other Federal agencies, and DOI. DOI estimates preliminarily that it may have as many as 26,000 sites requiring some cleanup. At many of these sites, responsibility would be shared with the parties who undertook the activities resulting in contamination. The most common site types are abandoned mines, oil and gas production sites. underground storage tanks, and landfills. To the best of DOI's current knowledge, the contaminants at these sites are primarily sedimentation in surface waters, acid mine drainage, chemically-reactive mining wastes, and industrial and household chemical wastes.
The current DOI estimate for completing cleanup is $3.9 billion to $8.2 billion in constant 1994 dollars. DOI does not yet have an estimate for the number of years to complete its cleanup program. DOI is funding cleanup activities at eight sites in FY 1995 through its Central Hazmat Fund (CHF), a centralized no-year fund for remedial investigations/feasibility studies and cleanups at hazardous waste sites for which DOI may be liable. DOI may fund activities at these and additional sites during FY 1996 using the CHF, contingent upon the final funding levels. Additional site cleanup activities are funded through the appropriations of the DOI bureaus with responsibility for the sites.
Department of Agriculture.
USDA estimates that there may be 3,500 potential CERCLA or RCRA sites on lands it manages. Ninety-six cleanup projects were completed at such sites in FY 1994, while 272 sites were investigated and another 70 were identified as needing investigation. Of its estimated 25,000 abandoned and inactive mining sites, USDA estimates that only about 10 percent are likely to require environmental cleanup under CERCLA. Many of these sites occur on land under USDA’s management, but, as with DOI, the contamination may not have been caused by USDA's operations. The most common site types are abandoned mines and landfills. Hazardous wastes from mining, chemical wastes, and sedimentation in surface waters are the primary contaminants at these sites. Not all agencies within the Department have completed their final inventories of potentially contaminated sites. Once these are completed in 1996, the estimate will be revised. The present USDA estimate for completing cleanup is $2.5 billion, in constant 1994 dollars. Some part of the total is anticipated to be paid by private sector responsible parties, particularly in case of abandoned mines at or adjacent to national forests.
Overall, its program is at an early stage of development, with basic site inventories remaining to be completed by the responsible agencies within the Department. USDA plans to complete its site cleanup program within the next 40 years and natural resource restoration within the next 50 years.
FEDERAL FACILITIES PROFILE
|
DOE |
DOD |
DOI |
USDA |
NASA | |
|
Nature of Contamination |
Radioactive, hazardous and mixed waste and fissile material |
Fuels and solvents, industrial waste and unexploded ordnance |
Mining, municipal and industrial wastes |
Hazardous, mining and chemical wastes |
Fuels and solvents and industrial waste |
|
Number of potentially contaminated sites and major site types |
10,000 sites |
21,425 sites |
26,000 sites |
3,000 sites |
730 sites |
|
Number of potentially contaminated facilities |
137 |
1,769 |
NA |
NA |
17 |
|
Number of active sites |
10,000 |
11,785 |
$3.9-$8.2 billion |
$2.5 billion |
$1.5-2 billion |
|
Current estimate to complete cleanup* |
$200 to $350 billion |
$26.2 billion |
$3.9-$8.2 billion |
$2.5 billion |
$1.5-2 billion |
|
Estimate being revised |
Released March 1995 |
Yes |
None scheduled |
Yes; due FY 1996 |
Yes; due FY 1995 |
|
Estimate of years to finish cleanup |
30-75+ yrs |
20 yrs |
NA |
10 yrs - landfills |
25 yrs |
|
Annual budget:*** |
$6.1 billion |
$2.5 billion |
$61 million |
$16 million |
$34 million |
|
Current funding source |
Federal |
Federal |
Federal |
Federal |
Federal |
|
Responsibility for contamination |
Agency |
Agency |
Agency, private parties and local governments |
Agency, private parties and local governments |
Agency |
|
Maturity of program |
Adolescence |
Mature |
Infancy |
Adolescence |
Mature |
|
FY 95 FTEs (Cleanup): |
3,108 |
NA |
NA | 82 NA | 25 160 |
4. Cooperative Efforts Among Agencies.
In addition to single-agency efforts, some agencies have worked to ether to clean up sites. For instance, the Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) is working with DOD on cleaning up the Crab Orchard National Wildlife Refuge in Illinois and the Rocky Mountain Arsenal in Colorado, and the National Park Service (NPS) and DOD are working together at the Presidio in San Francisco. In addition, DOD has teamed up with DOI bureaus, such as the Bureau of Land Management, the FWS, the NPS, and the USDA's Forest Service to deal with unexploded military ordnance and industrial explosives on lands managed by DOI and the Forest Service.
B. Building Knowledge About Relative Risk at Sites.
It may seem a simple expectation and task for agencies to complete risk assessments of all sites, but this task has proven a sizeable and expensive, yet essential, undertaking. DOE and DOD are the two Federal agencies that have made the greatest progress the effort to assess and evaluate risks. The other agencies are still in earlier stages of locating, assessing, characterizing, and evaluating the relative risks of their sites.
There nonetheless has been increasing progress in developing our understanding of risk at Federal facility sites and improving the risk-assessment protocols by which remediation decisions are made. The collective level of knowledge and experience in the use of risk assessment and analysis continues to build, and the science of risk assessment continues to evolve and be refined. It has been, and continues to be, very difficult to make detailed and accurate comparisons of relative risk across agencies, both because available information has been so limited and because the nature of risks varies so greatly from one agency to another. For example, EPA human health risk assessments for Superfund focus on cancer risk, while OSHA assessments focus on worker safety and health. While the quality of available information is often inadequate to make quantitative assessments of risk and comparisons of relative risk across sites and agencies, it is possible to use qualitative approaches incorporating such data and knowledge as do exist, to inform our understanding of those risks. Of course, assessments of the nature and magnitude of risks must be combined with additional information about technical resources, social, economic, and political values, and other factors to evaluate cleanup options and priorities in making sound risk management decisions. [National Academy of Sciences, Building Consensus through Risk Assessment and Management of the Department of Energy's Environmental Remediation Program (Washinaton, D.C.: National Academy of Sciences, Jan. 1994), pp. 2-3.]
Extrapolating risk information across DOE sites is a difficult task. Even trying to establish priorities within one site, given the different kinds of environmental settings, contaminations of concern and ongoing activities, can prove quite challenging. For example, just one site might contain the following competing priorities: remediating an Operable Unit under Superfund, siting of a hazardous waste site under RCRA, or stabilizing nuclear materials under recommendations from the Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board. DOE, however, has a few sites that have presented tremendous risks to the public, workers, and the environment that are far in excess of those faced by other agencies. One of the most significant of these was the SY-101 tank at Hanford that emitted hydrogen gas and presented an explosion hazard until DOE installed a special mixing pump to recirculate the tank contents. DOE has aggressively taken actions to lower the risk associated with such urgent problems as SY- 101.
Ongoing, efforts within the last 18 months by the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), EPA, DOD, DOE, and an interagency working group of Federal agencies have produced new guidelines on risk assessment and priority-setting pertinent to environmental cleanup. At the request of DOE, NAS prepared a report to advise DOE on risk assessment and management. [Ibid.] This report, issued in 1994, concluded that greater use of risk-based decision making is both feasible and desirable. Based upon this report, as well as principles for risk assessment developed by an interagency task force headed by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP), DOE issued a set of risk principles in January, 1995, that are specifically tailored to DOE's waste management and remediation activities. The DOE principles are being used as interim guidance while comments are received. Separately, EPA Administrator Browner issued new guidance on risk characterization in March 1995, to promote "transparency, clarity, consistency, and reasonableness" in the agency's judgments about environmental and public health risk. [Memorandum from Carol M. Browner, EPA Risk Characterization Program, Environmental Protection Agency Jan. 21, 1995, (transmitting EPA Risk Characterization Policy and Guidance, Jan. 21, 1995).] EPA is now working with DOE to ensure that implementation of that guidance corresponds to DOE's interim guidance on risk. EPA also is improving risk judgments in cleanup through policy directives like its future land use guidance, issued in May 1995, which will help ensure that future land use is factored into risk assumptions and remedial decisions. These guidelines for assessing risk and tools for comparing risks across sites should strengthen decision making and better ensure that funds are being spent on the highest priority sites. In addition, there should be an increasing degree of consistency in relative risk judgments across Federal agencies as these new efforts are implemented.
In addition to the risk assessment efforts being undertaken by EPA, DOD, DOE and other Federal agencies, the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry evaluates the public health impacts of past, present, and future potential releases of hazardous substances from Federal (as well as non-Federal) National Priority List (NPL) sites through the conduct of Public Health Assessments and other health studies (e.g., community health studies, health surveillance, and medical monitoring.) The data from these efforts provide a complement to site risk assessments by assessing human exposure levels and health impacts in affected communities.
While the science of risk assessment has been advancing, so too has site-specific progress at each of the responsible Federal agencies. The magnitude and complexity of the problems are unquestionably greatest at DOE. DOD, with thousands of active sites, and NASA, with a limited number of industrial-type facilities, are the furthest along in assessing and addressing their sites. USDA and DOI, while making progress in many areas, are, by contrast, at the early stages of identifying and responding to their problems at sites with contamination caused by private parties, such as mining operations.
Progress also has been made in recognizing that risk analysis and risk reduction benefits must consider risks associated with the cleanup itself, such as risks to workers or natural resources that are created by proposed cleanup. The greatest risk at DOE facilities generally appears to be to workers. For example, the Department recently completed a comprehensive study of the potential environment, safety and health risks ("vulnerabilities") that arise from the storage of plutonium in its facilities. [U.S. Department of Energy, Plutonium Working Group Report on Environmental, Safety and Health Vulnerabilities Associated with the Department's Plutonium Storage, (Volume I.: Summary), September, 1994, pp. vii, 10-22.] Out of 299 potential risks discovered, the 15 most significant did not affect the public at all. Instead, the 15 greatest risks resulted from relatively small releases of plutonium into work areas. The study found no potential risks to the public or environment that were highly likely. The 22 potential risks with greatest consequences to the public or the environment that it did identify, such as large internal fires or explosions, earthquakes, or aircraft crashes, all had medium or low likelihoods of occurrence.
The risks at most DOD sites are better understood and appear similar to those occurring in private industry. Most DOD contamination results from past operation and maintenance practices involving the use of fuels and solvents. Contamination at other Federal agencies’ facilities has received much less study than at DOD or DOE; however, their risks generally are believed to be similar to those resulting from hazardous substance contamination in the private sector. ["U.S. General Accounting Office, "Federal Facilities: Agencies Slow to Define the Scope and Cost of Hazardous Waste Site Cleanups," RACED-94-73, April, 1994.]
Further progress is necessary to fully incorporate ecological risks into relative risk judgments. Even where risks to human health are low, there may be injury to natural resources, particularly at those sites that include extensive land areas that have been minimally developed or used. The extent of such injury is not fully known, because natural resource damage assessments have generally not received adequate funding. In addition, as in the case of worker risk, there needs to be more consideration of natural resource damage attributable to cleanup activities.
C. DOD: A Relative Risk Framework and Community Partnerships.
DOD is making significant progress in its cleanup program. However, since the inception of a dedicated funding source in 1984 by Congress, the Department has been unable to document risk reduction or meaningful cleanup progress attributable to its cleanup program. As a result, DOD implemented a relative risk framework in order to evaluate its progress in reducing threats to human health and the environment at its sites. Use of this framework as a management and decision-making tool, in combination with community outreach, promises significant program improvement.
1. Rational Site Prioritization:: The Relative Risk Framework.
The Department's concept for conducting relative risk evaluations was developed by an interservice working group within DOD comprised of representatives from the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Defense Logistics Agency. This simple, yet helpful, framework has been implemented department-wide.

Under the framework, sites are grouped into low, medium, or high risk categories. In making these judgments, DOD first considers the nature of the contaminant, the pathway (i.e., the likelihood of transport of contaminants by soil, groundwater, or surface water), and the possible receptors (portions of the public or environment that may be biologically affected). The results of this analysis are presented to members of the Restoration Advisory Boards (RABS) at DOD installations for their discussion and review. In designing the relative risk framework, DOD incorporated early stakeholder involvement in the process by using the RABs as a mechanism for discussing the relative risk ranking of sites at installations. RABs serve as a forum for exchanging cleanup information with concerned Federal and state officials and local stakeholders. The Department's plan is to expand the number of RABs that participate in the relative risk ranking of sites at DOD installations. RAB members are able to advise and provide input that may change the final ranking of a site at an installation. The involvement of RABs in the relative risk framework has helped to open an earnest dialogue and partnering between stakeholders and the Department at the local level. As a result, DOD has had considerable success when RABs have participated in relative risk ranking of sites at its installations.
In recent years, DOD has increasingly focused its cleanup funding strategy on efforts required by schedules and milestones in agreements in order to meet the Department's overall budget targets. This funding strategy resulted in more sites being covered under agreements, since it was the only mechanism to obtain funding. However, the Department's approach did not always ensure funding was allocated to the most urgent sites. Beginning in FY 1996, DOD began to transition to a budget based on reducing relative risk, while still meeting all legal agreements. In FY 1997, the Department will base its budget on reducing relative risk at sites while meeting schedules and milestones in legal agreements. Furthermore, the Department will work with the regulatory community to stretch cleanup schedules at lower relative risk sites until funding becomes available. For example, Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama, has 32 potentially contaminated sites; 9 of these sites require no further action. In 1994, a RAB was established with 14 members who were provided training on the DOD relative risk framework. The ranking of the sites at Maxwell Air Force Base, using the relative risk framework, was presented to the RAB for their discussion and review. Discussion of the relative site rankings was lengthy and spirited. However, the RAB agreed with the rankings as submitted by the installation. Funding for these sites in the FY 1996 budget was allocated based on priority as a result of the relative risk ranking. Several RAB members expressed their appreciation for the honest and open nature of the process. The members felt that the relative risk framework is a process the average citizen can understand.
2. Community Partnerships: RABs and Outreach.
Based on the recommendations of the Federal Facilities Environmental Restoration Dialogue Committee (FFERDC), DOD recognized a need to refine its basic community involvement policy for both active and closing installations. As a result, DOD began a process of establishing RABs at both closing and non-closing bases. RABs are intended to ensure that all stakeholders have a voice by enabling the early and continual flow of information among the affected community, the installation, State and Federal regulatory agencies, and local and tribal governments. DOD's policy requires that RABs be established at installations having sufficient and sustained community interest in the cleanup program. To determine sustained community interest, one of the following, criteria must be met: (1) installation closure involves the transfer of property to the community, (2) at least 50 citizens petition for an advisory board, (3) the Federal, State or local government requests formation of an advisory board, or, (4) the installation determines the need for an advisory board. [Department of Defense, Defense Environmental Restoration Program: Annual Report to Congress for Fiscal Year 1994, p. 6.] To date, DOD has established over 200 RABs at both active and closing installations. DOD is continuing to organize RABs at additional installations and formerly used defense sites (FUDs).
In addition, DOD continues to build partnerships through the Defense Environmental Response Task Force, whose membership includes representatives from DOD, EPA, Department of Justice, General Services Administration, National Governors Association, National Association of Attorneys General, and public interest groups. The task force's goals are to examine environmental issues associated with the restoration and reuse of closing, military installations and to expedite and improve environmental response actions at those installations. [Ibid, p. 19.]
Other regional and installation-specific partnering initiatives have resulted in increased openness in dialogue and decisionmaking, higher levels of trust, and more productive negotiations. For example, an innovative partnership agreement among the Navy and regulatory agencies at Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North Carolina, has helped form a single vision for the installation's environmental restoration and base realignment activities, saving both time and money. [Ibid, p. 24.] In 1994, the Navy realized the success of this partnering initiative through the development of a $2.5 million abbreviated work plan for the investigation of four operable units. Partnering facilitated the development of this comprehensive work plan, saved an estimated $300,000, and cut at least one year off the cleanup schedule. The overall decision-making process was accelerated by achieving consensus among the partnering teams to shorten the work plan review time.
3. Closing Bases: Implementing the President's Fast Track Cleanup Program
DOD's progress in priority setting and community partnering has been coupled with significant attention to economic redevelopment of closing bases, pursuant to the President's five part plan for economic revitalization of base closure communities, One part of this plan is implementing "Fast Track Cleanup," which is designed to remove needless cleanup delays at closing DOD installations. This approach involves establishing cleanup teams at closing bases, providing effective community involvement, making clean parcels of land available, and accelerating compliance with the National Environmental Policy Act.
DOD is conducting environmental work at 100 Base Realignment and Closure (BRAC) locations. DOD has established cleanup teams comprised of representatives from the installations, EPA, and the respective State environmental agencies at over 70 bases where property will be transferred. These teams have conducted bottom-up reviews of environmental programs and have developed BRAC cleanup plans for each installation. Furthermore, DOD has established RABs at 69 of the closing installations, which serve as focal points for community participation in the cleanup process. In addition, DOD has completed all of the clean parcel determinations required under the Community Environmental Response Facilitation Act for the BRAC 1988, BRAC 1991, and BRAC 1993 installations. [Statement of Sherri W. Goodman, Deputy Under Secretary of Defense (Environmental Security), before the House Appropriations Committee, March 28, 1995.] This activity identifies uncontaminated parcels on closing installations, so that property can become available for rapid transfer for reuse.
In addition, performance measures are being established for environmental work at closing bases. The measurement effort will include categorizing the relative risk of sites and measuring the availability of property environmentally suitable for transfer. As a result, DOD will be able to measure its progress and success in implementing the President's Fast Track Cleanup Program.
D. DOE: Ongoing Process Improvements.
DOE is now implementing fundamental reforms in its programs and improving the performance of its environmental management and restoration activities. DOE has undertaken a major contract reform initiative to provide contractors more incentive to improve performance and contain costs. DOE has increased the number of staff devoted to contractor oversight and cost-estimation; it has made much greater efforts to identify and adopt best practices from industry and to share knowledge across sites; it has pressed for contract reforms to improve efficiency among its contractors; and it has accelerated efforts to explore innovative cost-savings measures, such as privatizing the remediation of tanks containing liquid radioactive waste by competitively contracting out on the basis of fixed unit price for treated waste. DOE has created Site-Specific Advisory Boards (SSABS) to increase local stakeholder knowledge of, and participation in, the cleanup process. Discussions with the advisory boards include the formulation of strategies based on reasonably anticipated future land use. Additionally, DOE has just completed its first comprehensive assessment of program costs and risks across the DOE complex, which has more closely tied priorities to risk and cost factors.
1. Contract Reform Initiatives.
Consistent with the recommendations of the National Performance Review, DOE has begun to implement a comprehensive strategy for contract reform. Among the measures being implemented are: recompetition of management and operations (M&O) contracts; increased use of fixed-price contracts as alternatives to traditional cost-reimbursement contracts; development of clearly-stated, results-oriented contract performance criteria and measures; and stronger incentives and disincentives for contractors in the areas of cost reduction and cost avoidance, timeliness and performance, and worker health and safety. DOE is also instituting more rational procedures for Departmental and contractor "make or buy" decisions, streamlining its procurement process, and reducing the use of contracts for support services. This restructuring of contract incentives seeks to ensure that contractors are accountable for and bear the costs of poor performance. Under existing M&O contracts, those costs frequently have been borne by taxpayers.
DOE is implementing its new contracting approaches at its Rocky Flats Plant in Colorado, which converted from nuclear weapons production to environmental cleanup and waste management in 1992. The strategy includes use of a mix of contractors and contract types, including fixed-price contracts, results-focused performance goals, performance-based criteria and measures, use of contractor incentives, increased contractor accountability, and government/private-sector partnership arrangements for project integration. In addition, at the Idaho National Engineering Laboratory, DOE has issued a contract consolidating five separate M&O contracts into one, with a strong emphasis on performance, results, and cost savings. In both cases, DOE is inviting substantial contractor innovation in defining how the work is to be designed and accomplished.
A number of specific contract cost areas have been identified in recently completed studies as significant potential sources for cost savings. Some of these studies [Including DOE's "Benchmarking for Cost Improvement", September 1993 and "Project Performance Study", November 1993.] have evaluated broad cost categories such as overhead (which can be particularly problematic in cases where some of the work is done by subcontractors), indirect, and project management costs. They have concluded that the cost of Federal cleanup is generally higher than the cost of comparable non-Federal work. Other studies, [These studies include GAO's "Energy Management: Types of Allowable and Unallowable Costs Incurred under Two DOE Contracts," January 1993, and "Nuclear Waste: Hanford's Well-Drilling, Costs Can Be Reduce," March 1993, and DOE Office of Inspector General Report "Audit of Health Benefit Costs at the Department's Management and Operating Contractors," June 1994.] including some undertaken by the U.S. General Accounting Office (GAO), have focused on very specific costs, often at a limited number of sites and determined that some cost items were excessive.
DOE also is undertaking numerous initiatives to improve contract management by improving its own workforce skills and management information systems for contract oversight and administration. [U.S. General Accounting Office, "Department of Energy: Challenges to Implementing Contract Reform, " RACED-94-150, March 1994.] The initiatives involve strengthening DOE financial and accounting systems; improving management of various categories of costs, including indirect costs; and modifying DOE's cost-reimbursement policies. The latter initiative will lead DOE to pay for contractor results rather than incurred costs, to reduce reimbursement of contractor-incurred fines and penalties, and to rely on the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) in lieu of DOE's acquisition regulations (DEAR). [Ibid., pp. 57-61.] DOE also will reduce the costs of contractor litigation through creation of a formal litigation management plan, tight guidelines for contractor retention and use of litigation counsel, and closer oversight and control of litigation decision-making.
2. Reducing Costs Through Efficiency Gains.
Personnel costs represent a large portion of total DOE contract costs and reductions in personnel represent an important source of potential savings. As DOE facilities move from nuclear weapons production to environmental restoration, the number and distribution of production and restoration contract personnel is changing. In some cases, however, the trend in the number of personnel has not matched intuitive expectations. For example, a recent DOE Inspector General report found that the M&O contractor at Savannah River had increased its staff by over 4,000 employees since 1989, even though all of the production reactors and Naval fuel facilities had been shut down. [U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Inspector General, "Report on Audit of Staffing Requirements at the Westinghouse Savannah River Company," January 1994.]
DOE has undertaken several initiatives to reverse this trend. First, as part of a pilot project organized under the Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA), DOE was authorized to hire 1,600 additional FTEs through contractor conversion. Of the first 1,200 allotted, 850 were allocated to field operations. These 1,200 positions, most of which have now been filled, will help achieve cost savings and improve cleanup contract management and oversight. An evaluation of this effort will provide more definitive answers on its success in achieving these goals. In addition, as part of a far-reaching agency strategic realignment and restructuring, DOE is streamlining its headquarters organizations and processes to reduce excessive overhead and oversight. Much like DOD, DOE will be focusing its headquarters efforts on determining policy and overall strategy, leaving field managers responsible for implementation of cleanup. Finally, in early 1995, DOE announced its intent to reduce its number of contractor personnel by 39,500 (from FY 1992 levels).
In addition, in FY 1995, DOE sponsored the first "workout" -- a site-specific discussion between the Department and its regulators to identify opportunities to improve cost efficiency. To date, workouts have been held for Hanford and Savannah River. The Hanford workout identified $1 billion in FY 1996-1998 savings, without compromising compliance with existing laws and regulations. Similarly, the Savannah River workout identified FY 1997 potential savings between $80 - $140 million, again without compromising compliance with existing laws or regulations. EPA has strongly endorsed the application and acceleration of these site-wide reviews to other DOE major facilities.
3. Encouraging Innovative Public-Private Partnerships.
New contractual relationships with the private sector are also developing. The EM program office has completed a feasibility assessment of privatizing the Hanford tank waste remediation system. Under this approach, the privatized contractor would be responsible for facility design, licensing, financing, construction, operation and treatment of the tank waste facilities. The contractor would be selected through competitive procurement on the basis of a fixed unit price for treated waste. The Hanford M&O contractor would continue to oversee the tank waste storage and to retrieve the waste from existing tanks for treatment by the privatized contractor. The proposed approach is divided into two phases - a commercial demonstration phase that would process about two tanks of waste and, if successful, a second full-scale treatment phase. EM is now negotiating revised milestones with the regulators.
In addition, DOE recently convened a broad stakeholder process to prepare recommendations concerning further privatization of DOE operations. These recommendations are anticipated in October 1995. Another DOE proposal under consideration could accelerate deactivation (removal of radiological and hazardous waste contaminants) from non-operational DOE facilities and save money. Under this proposal, DOE would hire private firms to deactivate buildings, where the private firms would supply the necessary funding for the project. DOE would pay the contractor over a period of years from the surveillance and maintenance cost savings, that result from deactivation. Payment would not begin until deactivation had resulted in cost reductions. The savings would be shared between the government and the contractor as specified in the contract.
4. Stakeholder Involvement Initiatives.
One of DOE's six strategic goals for its EM program is to establish a stronger partnership between the Department and its stakeholders. DOE established the Office of Public Accountability in 1993, which has coordinated the effort to form 10 SSABs across the DOE complex. These boards are designed to foster meaningful decisionmaking by advising DOE management on site-specific issues, such as future land use and remediation priorities within the site budgets. They are comprised of representatives of the local community, local government, environmental groups, Indian tribes, and State and Federal regulators. SSABs are becoming more and more critical to site-specific planning and priority-setting processes. This year, for the first time, stakeholders are actively advising DOE officials on the formulation of the FY 1997 budget. Stakeholders are given access to detailed budgetary, technical and planning data so that they may offer informed opinions on site priorities, resources allocations, and possible tradeoffs.
The EM program has realized tangible benefits from stakeholder involvement. [U.S. Department of Energy, Environmental Management 1995--Progress and Plans of the Environmental Management Program, pp. 10-12.] For example, the Department and regulators recently canceled the proposed closure of one waste area at Oak Ridge National Laboratory after stakeholders expressed concerns about the high cost and minimal benefits involved in the closure. Stakeholder involvement in the renegotiation of the Hanford Tri-Party Agreement enabled the Department to change several critical aspects of the Agreement. [Ibid, p. 11 .] Stakeholder involvement at the Fernald, Ohio site enabled the Department to save over $1 billion by stakeholders agreeing to accept less exacting cleanup levels than originally proposed. [Letter, Fernald Citizens Task Force (A U.S. Department of Energy Site-Specific Advisory Board) to the Secretary of Energy and DOE's Assistant Secretary for Environmental Management, April 11, 1995.]
The EM program has also begun involving stakeholders in the areas of environmental justice and managerial policy. Recently, the EM program released a draft paper outlining an environmental justice public participation strategy for public comment. A major objective of such a policy is to ensure that the Native American and other disadvantaged communities around cleanup sites are responsibly included in regulatory negotiations. The EM program also reconstituted the Environmental Management Advisory Board, which will serve as a board of directors to advise the EM Assistant Secretary on various program issues. The board is comprised of 28 representatives from labor, EPA, tribes, States, and citizen groups.
The process of stakeholder involvement at DOE is a dynamic one that continues to evolve. Stakeholder contributions are especially important in the areas of site-based risk assessments, future land use determinations, resource allocation decisions, and the ongoing assessment of environmental priorities.
5. Comprehensive Managerial Risk Assessments.
Defining the scope and severity of an agency's cleanup challenge may seem a natural prerequisite to development of a departmental remediation plan and subsequent related sound decisionmaking. Since the most significant contaminants for DOE have not been chemical, but radiological or mixed in nature, completing a baseline assessment at DOE proved a much more difficult, expensive, and technical undertaking than for any other agency. This unavoidably brought the Department significant criticism for expending so much Federal money for risk assessment, remedial investigations and feasibility studies instead of actual cleanup. The growing demand for noticeable progress in site remediation is, of course, in tension with the need for better scientific understanding of remedial options.
In FY 1995, however, the funding trend was finally reversed, with a greater percentage of Environmental Restoration funding now going toward remediation than to assessment. In March of 1995, DOE released the Baseline Environmental Management Report (BEMR) which for the first time catalogues the scope of DOE's environmental contamination. For DOE, the BEMR report identifies a total of approximately 10,500 potential release units from which contaminants could migrate into the environment. Many, but not all, of these units have been assessed for their contamination potential, but only one quarter of them have been fully characterized. [U.S. Department of Energy, Estimating the Cold War Mortgage; The 1995 Baseline Environmental Management Report, p. 3- 1.] In some areas, such as the permanent isolation of high level waste in a geologic repository, the problem is well understood, but the solution is not available at present, nor will it be until at least the year 2015. In other cases, such as soil contamination from underground testing in Nevada, no remedy is available or even on the horizon. [Ibid.] Thus, the full scope of the problem is still not completely defined and great uncertainty still exists in the estimate. Nevertheless, it is one of the first department-wide comprehensive at examinations of the balance among risk, costs, benefits, and land reuse. The fact that resources are increasingly being devoted to cleanup instead of assessment indicates that the boundaries of the DOE challenge are much better defined and real cleanup is in progress. Certainly, the baseline analysis will assist DOE decisionmakers and interested stakeholders in determining how best to put available resources to work.
IV.Paying the Cold War Mortgage: Remaining Challenges
A. The Potential Funding Gap
1. Scope of the Estimate.
The Federal government is spending about $9 billion a year to address the waste problem. As the table below shows, there is still much work to be done. The total outstanding cost is estimated to range from $234 billion to $389 billion over the next 75 years.
|
Table 1. Total Estimated Cost for Complete Cleanup by Agency (Billions of Dollars)* |
|
Department of Energy |
$200-$350 |
|
Department of Defense |
$26 |
|
Department of the Interior |
$4-$8 |
|
U.S. Department of Agriculture |
$2.5 |
|
National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
$1.5-$2 |
|
Total |
$234 to $389 |
The estimated range for the total cost was developed by aggregating existing agency estimates and analyses. While there was an attempt to define "cleanup" in a roughly standard way, no attempt was made to apply a common methodology, because of the tremendous variation among the different programs. Agency cleanup programs differ widely in maturity, extent of contamination, level of information available, cleanup methods, technical feasibility, and ultimately even the level of actual cleanup that is likely. The range provided is broad mostly because of uncertainties in DOE's future costs. Total cost estimates are likely to change over time as knowledge and experience improves. However, the sheer magnitude of the projected costs in relation to the annual total discretionary Federal budget (about $550 billion annually) underscores the imperative to allocate Federal resources wisely and efficiently.
The estimate covers the cost to clean up contamination from past activities at Federal facilities at all but DOI sites. All agency estimates include costs for studies, remedial design, and remedial actions. The estimated costs of decontaminating and decommissioning facilities, including compliance with legal requirements and environmental work at closing military bases (except for BRAC I sites), are also included in the overall estimate. Environmental technology development costs are included for DOE and DOD because of their significance to the total program. Technology development costs for other agencies are minimal and are therefore not included in the estimate.
Estimates do not, in general, include the costs of day-to-day compliance for ongoing waste management operations, which represent another large claim on our nation's resources and compete with cleanup. However, because of the indestructible nature of radioactive wastes, DOE must by necessity isolate these wastes virtually in perpetuity. Its cleanup estimate therefore includes the cost of treatment, storage, and disposal for the current inventory of stored waste, waste from continuing operations, and waste derived from remediation activities at sites such as Hanford, Washington, that do not have active ongoing government missions. Although DOE's EM program classifies all of these legacy and non-legacy waste operation costs as compliance costs, they are included in DOE's total cleanup costs to better capture the scope of the DOE challenge. Other agencies do not have such costs and so their cleanup estimates do not include costs for compliance. Estimates for DOD, DOE and DOI do include long-term maintenance and operations costs for remediation altematives. [Operation and maintenance costs include costs for labor, power and replacement parts.] These costs can be substantial depending on the remedy selected. For example, these costs represent nearly 17 percent of DOD's total cost for cleanup. USDA Forest Service costs do not reflect the possible recovery from potentially responsible parties (PRPS) on Federal lands or private operators' performance of cleanup contamination related to their activities.
2. Historical and Current Funding Levels.
Since the formal inception of agency environmental cleanup programs, the Federal government has budgeted almost $54 billion for Federal facilities cleanup through FY 1996. Annual expenditures grew rapidly through FY 1994, but the rate of budget expansion has now leveled off or is decreasing. About two-thirds of the total sum budgeted has been targeted at DOE facilities and includes amounts for ongoing waste management.
A breakdown of the Federal facility cleanup over the last five fiscal years is shown in Table 2 below.
|
Table 2. Federal Facilities Cleanup Budgets |
|
Agency |
Total to FY ‘91 |
FY ‘92 |
FY ‘93 |
FY ‘94 |
FY ‘95 |
FY ‘96 |
Total thru FY ‘96 |
|
DOE |
9,362 |
4,434 |
5,737 |
6,139 |
5,938 |
6,592 |
38,402 |
|
DODa/ |
4,077 |
2,108 |
1,604 |
2,484 |
1,998 |
2,079 |
14,350 |
|
DOI |
59 |
70 |
62 |
61 |
65 |
65 |
382 |
|
USDAb/ |
52 |
26 |
16 |
16 |
16 |
45 |
171 |
|
NASA |
47 |
20 |
27 |
34 |
24 |
37 |
189 |
|
EPAc/ |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
34 |
35 |
36 |
105 |
|
ATSDR |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
18 |
19 |
19 |
56 |
|
Total |
13,597 |
6,658 |
7,446 |
8,786 |
8,295 |
8,863 |
53,655 |
a/ Includes funding from the Defense Environmental Restoration and
Base Realignment and Closure Accounts
b/ Central account for
RCRA/CERCLA
c/ Office of Federal Facility Enforcement
3. Anticipated Funding Constraints.
Federal agencies can spend money only within the spending authority provided by Congress. Discretionary funding is controlled through annual appropriations bills. The Balanced Budget and Emergency Deficit Control Act of 1985 limits discretionary spending by placing caps on budget authority and spending for each fiscal year. If appropriations would exceed the budget cap, the Act establishes a procedure for across-the-board budget cuts. In recent years, Congressional action, through the adherence to budget caps on appropriations bills, has limited the funding available for cleanup, as well as for many other needs of the Federal government. Congress makes funding decisions among many priorities, including the amount of funding to comply with Congressional mandates to agencies to meet environmental cleanup requirements. Thus, unlike non-Federal and private sector entities, the financial ability of Federal facilities to comply with Congressional mandates is determined by the President and Congress.
Balancing budgetary objectives is particularly constraining for DOE, in light of the obligation to meet the requirements of over 70 active compliance agreements entered into with EPA and various States. As DOE has refocused its attention from weapons production to environmental management, the budget for environmental management grew by an average of 27 percent per year from $1.8 billion in FY 1989 to almost $6 billion in FY 1995. However, if we take into consideration the transfer of significant program responsibilities from other DOE program areas, resources in FY 1996 actually decrease from FY 1995 in nominal and constant dollar terms.
In the next five years, DOE will face the most significant challenge of any agency in being able to stay within budget targets established by the Administration. The EM program's revised targets go from $6.6 billion in FY 1996 to $5.5 billion in FY 2000 in current dollars ($4.8 billion in constant 1995 dollars) -- a reduction of 27 percent in constant dollars. Nevertheless, EM's responsibilities will continue to expand in coming years. For example, EM must decontaminate and decommission an enormous and growing backlog of facilities deemed surplus by other DOE program areas. EM continues to assume responsibility for high priority DOE missions such as foreign spent nuclear fuel management and plutonium stabilization. EM will also need to fund and build mixed waste treatment facilities to fulfill its obligations under RCRA. All of these activities compete with other Federal programs within a limited amount of discretionary funds.
The chart below presents a comparison between the five-year base case in the recently released Baseline Environmental Management Report (BEMR) cost estimate and the President's FY 1996 budget and outyear projections.
Table 3. DOE Federal Facilities Cleanup: Five-Year Projections
(Current dollars in billions)
|
FY 1996 |
FY 1997 |
FY 1998 |
FY 1999 |
FY 2000 |
5-Year Total | |
|
BEMR Estimates |
6.8 |
7.1 |
7.7 |
8.0 |
8.2 |
37.8 |
|
President’s Budget Estimates |
6.6 |
6.3 |
5.5 |
5.5 |
5.5 |
29.4 |
|
Annual Difference |
.2 |
.8 |
2.2 |
2.5 |
2.7 |
8.4 |
|
Cumulative Difference |
.2 |
1.0 |
3.2 |
5.7 |
8.4 |
BEMR base case projections assume a 20 percent increase in productivity improvement over the next five years. Even with these aggressive efficiency goals, the remaining budget shortfall will require major additional changes to the way DOE does business. The EM program plans to achieve significant progress in streamlining the DOE contractor workforce, reducing indirect and overhead labor costs, and contract reform; but these may be an insufficient source of savings to stay within the prescribed resource levels.
In DOD's case, reduced appropriations for Defense Environmental Restoration Account (DERA) during the past three fiscal years have led to renegotiations of cleanup milestones each year. DOE has also begun the process of reevaluating and, where necessary, renegotiating cleanup agreements to incorporate greater sensitivity to cost, risk, and technological feasibility.
B. Historical Management Obstacles to DOE Program Improvement.
Critics have lodged charges of ineffectiveness and inefficiency with the management of Federal facilities cleanup effort since its inception. [cf. Pasternak, Douglas with Cary, Peter, "The $200 Billion Scandal at the Bomb Factories," U.S. News & World Report , December 14, 1992, pp. 34-47; General Accounting Office, op. cit.] A look at the difficulties faced by one department, DOE, follows. The case of DOE is instructive because the magnitude of its remediation challenge and the rapidity with which its cleanup program had to be developed led to a number of management problems. Regulators have long held that a large portion of DOE's potential budgetary shortfalls could be funded through a detailed review of DOE's own programs for management productivity and streamlining gains. As previously described, DOE and other agencies involved in cleanup have themselves identified many inefficiencies and are in the process of addressing them. A summary of major problems now being address by the Clinton Administration is provided below.
1. Use of Inefficient Contracting Methods.
The Clinton Administration's National Performance Review (NPR) concluded that government agencies have not used available contract instruments as effectively and efficiently as they might, contributing significantly to the overall cost of the Federal facilities cleanup program. [National Performance Review, "Department of Energy: Accompanying Report of the National Performance Review" (Washinaton, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, September 1993), pp. 5-13.]
Federal facilities cleanup is largely executed by independent contractors. Nearly 50 percent of the total FY 1994 Federal facilities cleanup budget for all agencies was spent on DOE contracts alone. [Based on the following calculation: numerator equal [67 percent (percent of DOE 1992 budget spent on contracts per NPR) X $6.1 billion (DOE FY 1994)]; denominator equal $8.8 billion (FY 1994 total Federal facilities cleanup).] Any savings realized through changes in DOE's contracting practices offer the potential for significant savings in the total Federal facility cleanup costs. A DOE Contract Reform Team established by Secretary O'Leary found significant and systemic weaknesses in DOE's historic contracting practices, including the absence of well-defined performance criteria and measures, the failure of DOE financial reporting systems to produce the information necessary to assess and manage effectively, and a lack of competition. [U.S. Department of Energy, Making Contracting Work Better and Cost Less: Report of the Contract Reform Team (Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Energy , February 1994), pp. 6-7.] The Contract Reform Team, the NPR, and numerous General Accounting Office reports found fault with excessive reliance on sole source, cost-plus-award-fee contracts over fixed-price contracts; use of nonstandard contract clauses; inadequate contractor oversight and cost-estimation capability and reliance on contractors to perform much of this work themselves; assumption of contractor risks; and lack of incentives for contractors to safeguard worker health and safety.
2. Inadequate Contractor Oversight and Independent Cost Estimation Capability.
Many of the concerns regarding contracting at DOE are related to the oversight and management of contractors. In the past, DOE's information systems have not provided the kinds of timely, accurate information needed by senior managers on a regular basis for program analysis, including comparisons within and across sites, and cost control. [Ibid., pp. 46-47.] In addition, according to the NPR, DOE's EM staff has been too small and, in some cases, has lacked the level of technical proficiency necessary to ensure contract performance. [Ibid, p. 7.] As of fiscal year 1993, only 1,780 Federal employees were overseeing 37,000 contract employees, a ratio of one to 21. There is $3 million in program funding for every Federal employee in DOE's EM program, more than for any other DOE program and significantly more than the $300,000 per Federal employee at EPA. [Ibid, p. 7.] An interagency review by OMB and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (COE) cited the lack of EM personnel with the appropriate skills as a primary reason for schedule delays and cost overruns, as well as the inappropriate use of contractors for performing what are essentially government functions. [Interagency Review Group, "Interagency Review of the Department of Energy Environmental Restoration and Waste Management Program, Final Report" (April 29, 1992), pp. iv, 32-36.]
3. Limited Use of Innovative Productivity Improvement and Cost-reduction Practices.
A 1992 U.S. -News and World Report cover story, "The $200 Billion Scandal at the Bomb Factories," reported after a six-month investigation that DOE's cleanup program was plagued with problems of uncontrolled costs, lax performance standards, excessive overhead and project management fees, managerial incompetence, contract fraud, and contractor coddling. [Op Cit.] Government studies that provided much of the basis for the story included an April 1992 report assessing EM financial management and budgeting by an interagency group led by OMB and COE. The report identified a large number of accounts where budget estimates for various activities were substantially overstated and found that all field offices had very high overhead and contingency costs. It also found that EM did not rigorously manage budget execution to ensure compliance with required milestones and that field offices had insufficient governmental personnel with skills necessary to independently prepare and review cost estimates and budget requests and to effectively oversee contractors. Reports in the early 1990s by the GAO, the Office of Technology Assessment (OTA) and the DOE's Inspector General have raised similar concerns.
Past studies have revealed significant cost differences among EM sites performing the same kinds of work, between EM and other government agencies like the COE performing the same kinds of activities, and between DOE and the private sector. For example:
A 1991 Office of Technology Assessment report [OTA, Complex Cleanup, op. cit.] analyzed costs for a number of completed remediation projects and found wide disparities from site to site for the same activities. For example, annual sample analysis costs per well at five sites ranged from $1,333 at Livermore to $11,500 at Richland; soil/sludge excavation per cubic yard ranged from $46 at Oak Ridge to $2,084 at Richland; cap installation per square foot ranged from $.42 at Kansas City to $7.63 at Savannah River.
The 1992 Interagency Group report [Interagency Review Group, "Interagency Review of the Department of Energy Environmental Restoration and Waste Management Program, Final Report" , op. cit. ] found that design and construction of a hazardous waste treatment facility at Los Alamos was estimated at $185 per square foot for one structure and $310 per square foot for a second; Los Alamos budgeted $220,000 per full time equivalent (FTE) for remediation personnel, while the COE budgeted $100,000 per FTE; construction of three impermeable barriers (RCRA caps) at Oak Ridge totaling less than one acre was estimated at $3 million, $2.5 million more than the COE would pay for the same work; contractor flight costs for 405 trips at Fernald were estimated at $331,750, more than 50 percent above the COE's estimate; 25 Computer Aided Drafting Design (CADD) stations at Fernald were estimated at $45,000 each, while top brand name CADDs cost only $18,000; temporary trailer office space was estimated to cost over $160 psf at Fernald compared to a $128 psf rate for quality permanent office space in Washington, D.C.
In response to OMB staff questions in fiscal year 1993, DOE reported considerable variation in average per hour direct labor costs across sites, for example: $32.20 at the Waste Isolation Pilot Project (WIPP), $51.06 at Oak Ridge for Bechtel employees on the Formerly Utilized Sites Remedial Action Program (FUSRAP), $56.90 for WINCO employees at Idaho National Engineering Laboratory, $70.70 at Sandia National Laboratory, $81.97 at Los Alamos National Laboratory, and $84.00 at Rocky Flats.
In fiscal year 1993, EPA field representatives reported that EM paid $15 million for eight RCRA facility investigation plans at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), in 1992, for which EPA typically pays about $500,000.
A 1993 study prepared for EM compared 65 EM remediation and waste management projects with key characteristics of over 1,000 other public sector and private sector projects. The study found that DOE costs for equivalent work were significantly higher than industry norms (32 percent higher than private sector and 15 percent higher than public sector), that EM's higher costs were a function of high project management costs and project system practices, that cost growth (average overrun of 48 percent) in EM projects is a result of poor project definition, and that EM schedules slipped by 52-69 percent on average compared with 16 percent for other projects. [U.S. Department of Energy, The Department of Energy Office of Environmental Restoration & Waste Management Project Performance Study (Reston, VA: Independent Project Analysis, Inc., November 30, 1993).]
These examples have prompted DOE to examine ways to effect better cost control. Detailed initiatives planned in the areas of contract and management reform are addressed in Chapter 5.
C. The Need for Statutory and Regulatory Reform.
The inefficiency and waste that historically have been attributable to management of the cleanup effort at Federal facilities have been compounded by particular uncertainties and inefficiency associated with the statutory and regulatory framework governing these cleanups.
1. Overview of the Regulatory Framework.
Federal facility cleanups are currently governed by CERCLA, the corrective action requirements of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), the Atomic Energy Act (AEA), and State laws and regulations, but are concurrently subject to the constraints of the budget and appropriations process. The relevant environmental laws and their role in the cleanup process are briefly described as follows:
CERCLA generally imposes cleanup and reporting requirements for cleanup of facilities where there has been a release or threatened release of hazardous substances. It imposes liability for both the costs of response (removal and remedial action) and natural resource damages. In the context of Federal facilities, EPA and the lead Federal agency enforce CERCLA administratively. EPA's enforcement effort, however, is generally limited to those sites that are on the National Priorities List (NPL), where EPA must concur in remedial actions selected by the Federal agencies.
With respect to radioactive materials, the AEA and subsequent legislation authorize DOE to establish, oversee, and enforce compliance with nuclear health and safety requirements at its facilities. This has been done through an extensive series of departmental orders and regulations that set standards for all aspects of the operation, maintenance, and cleanup of nuclear facilities.
Federal agencies also are subject to independent regulation by State, tribal, and local regulators for all environmental media. Both CERCLA, RCRA and other Federal environmental laws subject Federal agencies to substantive and/or procedural requirements of Federal, State and local environmental laws.
2. Statutory and Regulatory Impediments to Sound Management.
The statutory and regulatory provisions governing the cleanup process have presented significant uncertainty to those managing Federal facility cleanups, with commensurate effects on the efficiency and soundness of cleanup management. The interaction and interrelationship among different regulatory mechanisms may cause significant state-to-state and site-to-site variation in cleanup standards and requirements, and potentially duplicative processes of cleanup decisionmaking and regulatory oversight. For instance, the CERCLA remedy selection process requires the application of applicable or relevant and appropriate requirements (ARARs) found in other laws, even where those laws were not developed as remediation standards. This may generate differences in the cleanup standards that apply at sites located in different states and has resulted in contention and uncertainty about which requirements are "relevant and appropriate" at any given site.
These uncertainties are compounded by the potential overlay of one regulatory authority upon another. States have invoked their authority under RCRA or state law at superfund sites, and in some cases have imposed additional requirements beyond those required under CERCLA. Conversely, a site that is being remediated under a state RCRA or other program may be subject to listing on the NPL under CERCLA, introducing a different regulator and different cleanup criteria. At either type of site, contaminated media generated by the cleanup itself may be deemed "hazardous waste" subject to the separate panoply of RCRA regulations for hazardous waste transport, treatment, and disposal, even where cleanup of those wastes present extremely low risk.
Integration of different regulatory regimes has been made more difficult by the fact that, within each regulatory regime, the role of cost in cleanup decisions has been neither transparent nor consistent. Hampered by the limited information about risk available in the early stages of their programs, agencies were slow to set priorities among sites according to comparative risk. Even yet, they remain uncertain about whether those priorities can be implemented in the context of competing priorities set by different regulators, many of which are reduced to compliance agreements among the agency, EPA, and the state. Agencies also have been slow to develop risk assessment and risk characterization methods that are adequate to the task of implementing statutory cleanup goals according to sound science and realistic risk assumptions at Federal facilities. For example, EPA just recently issued guidance to ensure that its remedy selection process explicitly takes into account the reasonably anticipated future land use at a site, which suggests that earlier decisions may have been based on unlikely future land uses, such as future residential use of an industrial site. Furthermore, there has been little guidance to ensure that risks to on-site remediation workers and ecological risks attributable to the remedy, itself, are taken into account when considering the risk-reduction benefits of different cleanup alternatives.
The role of cost, similarly, has been neither clearly nor consistently analyzed over the course of cleanup decisions for these programs. Consideration of future land use is one effective means of correlating cleanup costs with risk-reduction and other benefits, but the role of costs and standards of cost-effectiveness otherwise require better definition. Under CERCLA, courts have made clear that cost-effectiveness stands on an equal footing with other statutory criteria (such as the preference for permanence and treatment in remedies), [See NCP, 40 CFR 300.430.] but the statutory and regulatory requirements implementing these criteria have to date been subject to varying interpretation by different agencies. The development of additional approaches that address risks and costs in a categorical way -- such as presumptive remedies for particular types of sites and screening levels for specific contaminants -- has required significant time to develop and may have resulted in greater delay and cost at many Federal facility sites.
Finally, the absence of routine consultation between Federal facilities and the regulating agencies, and among agencies, regulators, and the affected communities has further impaired effective communication about risk and cleanup alternatives at sites. This has impeded the process of reconciling cleanup priorities with budgetary constraints, and diminished regulator and public understanding and confidence in Federal agency management of the cleanup process.
3. Role of Interagency Agreements (IAGs).
Section 105 of CERCLA designates the National Contingency Plan (NCP) as the source of procedures and standards for implementing the Act. Under the NCP, EPA develops an NPL list which identifies those facilities posing the greatest risk or danger to public health and environment. EPA uses a screening system required by CERCLA, the Hazard Ranking System (HRS), to select facilities for the NPL. EPA may designate a large Federal facility with multiple potential sources of contamination, even if they are miles apart, as one site on the NPL. As a result, EPA typically enters into an umbrella cleanup agreement for that facility or installation. The following occurs once a site is added to the NPL:
Section 120 of CERCLA requires that, within 6 months of the inclusion of a Federal facility on the NPL, the agency that owns or operates the facility must begin a remedial investigation and feasibility study (RI/FS). (Interim removal actions are permitted if there is a particular problem needing immediate attention while the RI/FS is being completed.)
Within 180 days of the completion of the RI/FS, the agency head must enter into an Interagency Agreement (IAG) with EPA for "expeditious completion... of all necessary remedial action at such a facility. It is the policy of EPA, DOD and DOE to enter into IAGs much earlier -- often shortly after a site is proposed for or listed on the NPL --- in order to develop a comprehensive agreement addressing both the investigation and remediation phases of the cleanup. Each IAG is required to include a review of alternatives and a selected remedial action for the facility, as well as a schedule for completion of the remedial action and arrangements for operation and maintenance of the site. EPA policy has been to have the State in which the facility is located be a party to the IAG as well.
Within 15 months of signing a record of decision for cleanup, an agency must begin substantial continuous physical, on-site remediation.
In the past decade, DOD and DOE, the agencies with the majority of Federal sites on the NPL list, have entered into 182 IAGs under CERCLA. [DOD has 112 installations listed on the NPL-- 88 active and 24 closure installations. All of DOE ’s major facilities are on the NPL. DOI has only two sites on the NPL, but it is also involved as a third party at numerous other NPL sites. USDA currently has two sites on the NPL.] The potential for conflict between the EPA's CERCLA authority and the States' hazardous waste regulatory authority has provided an additional incentive to negotiate three-party IAGs in order to establish a basis for consensus between the two regulators on cleanup strategy for a given site or facility. As a result, at Federal facility NPL sites, IAGs have become the principal mechanism for setting, cleanup priorities and schedules, each with legally enforceable milestones for project completion. Due to hurried efforts to establish IAGS, negotiators for both agencies and their regulators established milestones with limited knowledge about the nature and extent of the contamination, relative risks to the public and workers, future land-use of the site, or the feasibility and costs of remedial action. In many cases, agencies entered into agreements without appreciating future budget limitations that would constrain their ability to meet the terms and milestones in these agreements.
The evolution of available information creates an ongoing need to modify timetables and milestones in IAGS. The IAGs have provisions for modifying technical requirements and schedules as circumstances warrant through clauses governing force majeure, extensions, funding and modification; however, such changes must be agreed to by regulators and the involved agency. Although the majority of agreements are only a few years old, most have undergone minor modifications or major revisions. For example, the Hanford Tri-Party Agreement, signed in 1989, has had over 150 modifications and was recently renegotiated. In practice, achieving agreement on other than relatively minor modifications requires a significant commitment from all of the parties involved. As a result, more feasible timetables have often been difficult to achieve.
4. Tension Between IAG Process an Federal Budgetary Constraints.
Most IAGs assumed that funding levels for cleanup would grow at significant rates indefinitely. In 1993, however, Congress passed the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA), which caps total discretionary spending of the Federal government through 1998. Although individual programs are not directly constrained by OBRA, the intense competition for resources among all discretionary programs and the necessity to offset increases in one program with reductions in another have resulted in significant funding decreases for Federal facilities cleanup programs. Cleanup programs are now competing for funds with other agency missions, which may have their own legal or regulatory requirements. This change in the Federal fiscal environment requires greater use of existing flexibility to renegotiate IAG milestones to better reflect gains in technological developments and current funding levels available for the program.
Any effort to reconcile IAGs with the budget process must be conducted with consideration of the further requirements of Presidential Executive Order 12088 under which Federal agency heads are to "ensure that sufficient funds for compliance with applicable pollution control standards are requested in the agency budget." ["Executive Order 12088, Federal Compliance with Pollution Control Standards, 3 C.F.R. 243 (1979); as amended by Executive Order 12580, 52 Federal Regulation 2923 (1987).] This principle has been incorporated in most of the IAGs and other agreements in order to ensure agencies seek the full level of funding required to meet the milestones in agreements. This provision has frustrated the efforts of certain Federal agencies to submit budgets that satisfy both budget targets and the Executive Order, since the funding requirements for commitments within signed IAGs have often exceeded their budget targets. DOE, for example, has gone from average annual funding increases of about 25 percent from FY 1990 through FY 1993 to annual funding reductions from FY 1994 through FY 1996. As a result, a number of current IAG schedules or commitments may well need to be modified to reflect these new funding constraints. Otherwise, the result will be a tension between two competing mandates: Executive Order 12088 and the Budget Enforcement Act.
These are urgent problems with grave implications for the budget and for sound cleanup management. RCRA, as amended by the FFCA, waives sovereign immunity for civil and criminal penalties and state enforcement actions for failure to comply with hazardous waste management requirements. Accordingly, when shortfalls occur, agencies must resolve the conflicting priorities set via enforcement actions which are imposed by the multiple jurisdictions to which the agencies are subject. Civil penalty awards that might result from noncompliance threaten a further drain on available resources. Potential exposure to contempt citations or other sanctions threatens to distort agency priority-setting and undermine sound management.
In the past, when appropriations for cleanup were below the level requested by Federal agencies, shortfalls were generally distributed by determining which schedules in agreements could be renegotiated. Some agency agreements contained force majeure provision, which permitted agencies to renegotiate agreements based upon Congressional reductions. As shortfalls become more significant, however, this site-by-site process has begun to impede rational and systematic priority setting. Another approach, recommended by the FFERDC is generally to distribute the shortfall on a pro-rata basis to each site. [FFERDC is a Federal advisory committee chartered by EPA and composed of individuals affiliated with various Federal, State, tribal, and local govemment and other organizations concerned with Federal facilities cleanup. FFERDC has recommended a priority setting system that attempts to balance the concerns of Federal agencies, regulators and other stakeholders.] The FFERDC position is premised on the assumption that neither the President nor any agency should ever request less than the appropriation that would be necessary to meet all existing milestones. FFERDC believes that pro rata distribution of a shortfall is best, because existing data and science may be inadequate to determine objective, consensus cleanup priorities, and that factors other than human health and environmental risk need to be considered in allocating cleanup funds. ["Interim Report of the Federal Facilities Environmental Restoration Dialogue Committee: Recommendations for Improving, The Federal Facilities Environmental Restoration Decision-Making and Priority-Setting Processes" (Washinton, D.C.: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, February, 1993), p. 44.]
5. Funding Approaches for Federal Agencies.
Current Federal facility cleanup priorities are driven by statutes, regulations, and agreements that primarily emphasize comprehensive, thorough cleanup of individual sites and facilities. As a matter of Federal agency practice, Federal facilities listed on the National Priority List (NPL) take precedence over other non-NPL facilities. For non-NPL facilities, Federal agencies establish priorities for cleanup actions in different ways, although each generally attempts to direct funding to those contamination problems that pose the greatest threat to human health and the environment. In practice, other factors may significantly influence the allocation of cleanup dollars. These factors include priorities outlined in interagency agreements with regulatory agencies, risk/technological uncertainties, economic development goals, cultural values (e.g., environmental justice), cost effectiveness, and other agency missions. The method of prioritization and the allocation of funding to, within, and among sites varies from agency to agency.
At DOE, the allocation of funding is made first to stabilize those sites that represent a significant and urgent risk to human health and the environment -- the first of six goals for environmental management. The other five goals are: (2) providing a safer workplace; (3) addressing managerial and financial goals; (4) becoming more outcome oriented; (5) pursuing innovative technologies; and (6) implementing a public involvement process. In some cases, DOE has already used these program goals to identify its urgent sites and applicable technologies, and has begun corrective actions. Systematic, risk-based prioritization has been lacking throughout most years of the program. However, DOE has begun using data from its recently-completed draft risk report to identify its most urgent risks and guide its environmental management activities. [U.S. Department of Energy, Risks and the Risk Debate: Searching for Common Ground, "The First Step", Draft (Washington, D.C.: Office of Environmental Management, June 1995).]
DOD, similarly, has found that its current polices and practices do not always address the worst sites first. In recent years, DOD has increasingly focused its cleanup funding strategy on efforts required by schedules and milestones in agreements in order to meet the Department's overall budget targets. This funding strategy resulted in more sites being covered under agreements, since it was the only mechanism to obtain funding. However, the Department's approach did not always ensure funding was allocated to the most urgent sites. Beginning in FY 1996, DOD began to transition to building its budget based on reducing relative risk while still meeting all legal agreements. In FY 1997, the Department will base its budget on reducing relative risk at sites while meeting schedules and milestones in legal agreements. Furthermore. the Department will work with the regulatory community to stretch cleanup schedules at lower relative risk sites until funding becomes available.
D. The Special Problem of Radioactive Waste
Radioactive waste presents a great remediation challenge for the Federal government. Much of this waste will remain radioactive for many years -- up to tens of thousands of years. It cannot generally be neutralized, but must be contained instead. In many cases, treatment technology is not available.
Because of the potential impact upon many future generations, remediation plans must essentially provide for perpetual care of long-lived wastes and take into account unusual technical concerns of residual radionuclides. Even characterization of the waste has been difficult due to the health risks to workers. A lack of agreement upon the threshold level in soil, surface or groundwater which will prevent unacceptable risks to human health, as well as related uncertainties about future land use of former weapons production sites, pose major obstacles to DOE's efforts to conduct remediation at these sites. As DOE has pointed out in its recent Baseline Environmental Management Report (BEMR), decisions regarding land use, allowable residual contamination and technology advances will dramatically affect the cost, and, given limited resources available, the timetable for remediation.
1. The Implications of Perpetual Care.
When talking about environmental restoration of radioactive contamination, we often use the term remediation instead of cleanup. The reason is purposeful. Unlike industrial contamination which can be cleaned up and the wastes neutralized through burning, chemical processes, or biodegradation, radioactive contamination presents the much more difficult challenge of safely confining the radioactive waste until it decays sufficiently to the point that it no longer presents a threat to human health and the environment. Radioactive wastes generated in the production of nuclear weapons by DOE and its predecessors are classified into several categories depending on the hazards they pose, the length of time they remain radioactive, or their source. Low-level radioactive and low-level mixed hazardous and radioactive wastes, which represent the largest portion of DOE's cleanup burden by volume, present storage, and disposal uncertainties, even if they decay rapidly and are not initially highly radioactive. [Approximately 3 million cubic meters of low-level waste (primarily rags, protective clothing contaminated equipment, decontamination wastes, and scrap irradiated metals) currently exist, although more will be created in the future as we clean up radioactively contaminated sites. This waste is currently being disposed of at the Nevada Test Site, the Hanford Site in Washington, the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, Oak Ridge in Tennessee, Los Alamos in New Mexico, and the Idaho National Engineering Laboratory (INEL).] Within this category, mixed waste is particularly problematic, because of a lack of available treatment capacity or, in some cases, appropriate treatment technologies.
Highly radioactive waste presents a much greater technological challenge. Spent fuel and high-level waste from the nuclear weapons complex contain concentrated quantities of radioactive nuclides that decay very slowly. [Approximately 2,700 metric tons of spent fuel is currently stored by DOE principally at four sites: Hanford, Savannah River, INEL, and West Valley in New York. The commercial industry stores approximately 30,000 metric tons at more than 100 nuclear reactor sites around the United States. DOE currently stores about 100 million gallons of high-level waste, resulting from spent fuel reprocessing,, in 243 underground tanks in Washington, South Carolina, Idaho, and New York. Present intentions are to ultimately store both spent fuel and vitrified high-level waste in the permanent repository. Although not directly addressed, excess weapons grade plutonium (from the more than 100 metric tons produced in total during the Cold War) is also intended for storage in the permanent repository.] This poses a long-term hazard that requires disposal and isolation from the environment for thousands of years. Efforts are currently in progress at DOE to see whether Yucca Mountain, Nevada, is scientifically suitable to serve as a permanent repository for these high-level wastes. Transuranic wastes from defense plutonium activities also require similar permanent disposal until the radioactive elements decay sufficiently. [There are approximately 100,000 cubic meters of transuranic waste (any material used in plutonium processing, and containing significant quantities of plutonium, americium, or other elements whose atomic weights exceed those of uranium). This includes chemicals used in plutonium metallurgy, air filters, gloves, clothing, tools, piping, and contaminated soil.] DOE's near-term challenge is to store this waste safely until a deep underground geologic repository is available for permanent disposal. A separate facility near Carlsbad, New Mexico, called the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP), is in the process of certification for transuranic wastes. The fact that these highly radioactive and long-lived wastes will need to be confined and isolated as far into the future as we currently have recorded history emphasizes the complexity of the cleanup challenge.
A great deal of research has gone into finding treatment technologies suitable for stabilizing radioactive material for long periods of time and geologic conditions suitable for final repositories for radioactive wastes. Unfortunately, commitment to a single solution has on several occasions been diverted or weakened by suggestions that some new technological advance will provide a better answer. It is true that much of the field of material science is still quite immature as a science. Thus, although the effect of radiation upon the strength, as well as corrosion rate, of materials has been studied for over half a century, there is still uncertainty over whether materials stable over a number of decades will in fact be equally resilient over a period of 10,000 years. This uneasiness has delayed decision making and support for rapid development of these final repositories. In the short term, it generates difficult questions about the type of treatment necessary to make waste ready for acceptance into a long-term disposal facility. Efforts continue to ready the WIPP facility by 1998 and Yucca Mountain sometime before 2015, assuming it is found scientifically suitable.
The extent to which we safely protect human health and the environment from long-lived radionuclides, while also minimizing the financial and technical burden of nuclear waste disposal passed on to future generations, will in large measure depend on decisions made today. Choices on the type of land reuse, the length of time we are willing to wait to complete remediation, the cleanup levels required, and ultimately, the stabilization technologies selected, will be critical to cleaning, up radioactive contamination effectively.
2. Impediments to and Costs of Characterization.
At DOE sites with radioactive contamination, the need to limit radiation exposure of workers performing characterization radiation surveys drives up the cost of data collection. DOE's efforts to assess the level of contamination in cribs at Hanford serves as a good example of the complexity of their characterization challenge. In order to collect measurements to define the extent and nature of contamination in and around the cribs, a health physics technician would exceed many times the annual acceptable radiation dose. Therefore, in order to protect worker health, engineers must first develop a fairly sophisticated remote controlled radiation sensor to take the same radiation measurements. Developing the necessary technology delays characterization. At other DOE sites, radiation workers have been contaminated or injured while conducting maintenance activities and characterization studies. In addition, the amount of waste generated through the cleanup process is unknown. This makes it difficult to assess life value costs and risk impacts, as well as treatment, storage, and disposal costs.
Uncertainties also can remain regarding the extent of contamination at a site, even after the study and remedial design phases have been completed. For example, differences in sources of contamination, soil conditions, hydrogeology, and transport mechanisms make it difficult to completely characterize and understand actual conditions at a site. In fact, the full extent of the cleanup effort may not be known until the remedial action is put in place and the effect on the soil and groundwater is analyzed. Cost-effective remediation, however, will not occur without these studies, nor can resources best be allocated without knowing the extent and location of contamination at Federal facilities. The fact that relative risk assessment information is still generally incomplete and not integrated on a comprehensive site-wide basis, let alone used for cross-site risk comparisons, remains as one of the largest obstacles to cost-effective cleanup at many agencies. An additional impediment to assessing radioactive contamination at DOE sites is the lack of a framework to ensure consistency in relative risk assessment procedures across sites and to permit comparisons among them.
3. Ongoing Questions About the Biological Effect of Radiation.
The general lack of understanding by the public about the biological and environmental effects of radiation were brought about in large measure by the secrecy of the nuclear weapons program. This generated wonder, mistrust, and to some extent, even fear about "things nuclear". Meanwhile, scientists have studied the issue for over a century and have conducted a tremendous amount of research to study these effects. Many of their findings are fairly conclusive, but as with any research, there are some areas of scientific disagreement. Unfortunately, and inappropriately, this creates indecision in remediation plans which can result in unnecessary cleanup delays.
Scientists have known of the harmful effects of radiation upon the human body since the beginning of this century and may have devoted more scientific research to understanding radiation than any other known human carcinogen. From their work, it is clear that high doses of ionizing, radiation cause cancer. Yet, questions about the human health effects caused by low doses of radiation (less than 10 em) remain extremely controversial. [OTA, Complex Cleanup, p. 99.] Much of the early knowledge was gathered by reviewing overexposure cases of radium dial painters, underground miners, and X-ray therapy patients, in addition to animal studies. Later, studies of atomic blast victims at Hiroshima and Nagasaki, coupled with those of military personnel exposed to atomic bomb testing in the late 1940s and early 1950s, added to our knowledge about the immediate and long-term health effects of radiation. Since most of these cases were the result of exposure to fairly high levels of radiation, they did not produce useable information about prolonged exposure to low levels of radiation -- the kind of data that would produce the best standards for radiation exposure to the general public. Incorporating these observations of high-dose radiation effects into mathematical models for predicting low-dose effects therefore raises questions about the assumptions that must be made to extrapolate the low-dose health risk. [Ibid.]
Only in the last few decades has the accumulation of information for human studies on low-level radiation exposure (such as individuals exposed to nuclear weapons testing fallout, low doses of radiation during medical procedures, and high radiation background levels) permitted statistically significant sample sizes. These studies have not shown consistent or conclusive evidence of an associated increase in the risk of cancer. Attempts to observe increased cancer in human populations exposed to low doses of radiation have been fraught with difficulty and a lack of clarity. Discerning the risk of low-dose radiation from the risk effects of exposure to other hazardous or toxic substances has not proven easy. It is entirely possible, and indeed many within the radiation health physics area would agree, that this finding is actually supportive of the conclusion that there is no increased risk of cancer from exposure to low levels of radiation. The uncertainty about the risk from low-level exposure has prevented complete agreement about limits on public exposure to radiation.
There are even greater disagreements on the genetic effects of low level radiation exposure -- the effect of parents' exposure to radiation upon their children or grandchildren. The prevailing view is characterized by an intense study of nearly 70,000 offspring of atomic bomb survivors that failed to identify any increase in genetic effects. Other recent analysis also indicates humans now appear less sensitive to the genetic effects from radiation exposure than previously thought. However, a peer reviewed study published in 1990 reported an association between the risk of childhood cancer and a father's exposure to low-dose radiation among people living near the Sellafield nuclear reprocessing plant in Britain. [Ibid] Although not supported by any other similar studies, and itself criticized for its small sample size, the Sellafield study linked fathers' prior exposure to 10 to 100 rem to leukemia among their offspring. This finding, however limited, further illustrates how much controversy remains regarding the health effects of radiation. Another criticism of the available studies concerning radiation exposure is that they focus mainly upon cancer risk, not other potential adverse health effects that may result from the impact of, and interaction between, radioactive contaminants.
4. Gaps in and Lack of Agreement Concerning RadionuclidesStandards Complicates Remediation.
The above discussion about the uncertainty of radiation exposure risks helps explain our inability to agree upon a set of acceptable levels for residual radioactive contamination. Federal limits on public exposure to radiation, agreed upon by all Federal agencies, do not currently exist. This delays formulation of consistent standards for acceptable levels of residual radionuclides in soil and water when cleaning up contaminated Federal land. Without agreed upon standards, the most cost-effective cleanup technologies may not be chosen, and actual cleanup at facilities may be delayed.
Historically, the various Federal agencies with responsibility for developing radionuclide standards, principally EPA, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), and DOE, have taken different approaches to limiting human exposure to radiation. [GAO Report, "Nuclear Health and Safety: Consensus on Acceptable Radiation Risk to the Public is Lacking," RCED-94-190 (Washington, D.C.: U.S. General Accounting Office, September 1994), p. 9.] The science that supports the standards each agency has developed is complex, difficult, and multidisciplinary. It involves conceptual modeling of the interaction of low-level radiation with the surrounding environment and the human body. [Ibid, p.28.] These limits tend to rely more on assumptions than actual measurement. Agencies have also made different assumptions in their calculations. As a result, estimated risks to the public associated with agency guidelines vary considerably. [Ibid, p.1.] EPA and NRC have embarked on rulemakings on residual radioactivity standards, and they have agreed to use the same radiation exposure levels in setting the standards. The EPA standards would apply to DOE and other Federal agencies, while NRC rules would apply to all NRC licensees.
The current lack of consensus regarding the technical assumptions behind radionuclide standards has frequently resulted in overlapping regulation of licensees. In some instances, duplication requires clarification of responsibilities by regulatory agencies and leads to other inefficiencies. An example at DOE facilities is the joint regulation required of source, special nuclear, and byproduct material mixed with RCRA-regulated hazardous wastes. RCRA gives EPA or authorized States authority over the hazardous components of the waste, while the Atomic Energy Act (AEA) gives DOE authority over the radioactive portions. The distinction between the radioactive and chemical components of the same wastes means that DOE, EPA, and States share authority with a resulting lack of uniformity in standards. [David P. O'Very, The Regulation of Radioactive Pollution, ed. D.P. O'Very, C. Paine, D.W. Reicher (Boulder, CO: West View Press, Inc., 1994), p. 292.]
The lack of a unified radiation protection policy also leads to gaps in regulatory coverage. GAO noted in 1993 that several EPA regulations pertaining to the handling of radioactive wastes have been envisioned for years but not implemented because of problems with coordination and priority setting among agencies; principally EPA, DOE and OMB. [GAO Report, "Nuclear Health and Safety; Consensus on Acceptable Radiation Risk to the Public is Lacking," RCED-94-190, p. 21.] Thus, cleanup requirements are generally established separately for each operable unit undergoing cleanup at a DOE site. For example, DOE and EPA debated for three years over what standards should be used for one operable unit -- the K-65 silos --at DOE's Fernald installation. No standards existed concerning how to manage and dispose of the concentrated uranium ore in the silos, and consequently, EPA and DOE staffs required significant time to resolve the issue. Cleanup was delayed, and valuable management time was expended inefficiently. [GAO Report, "Nuclear Cleanup; Completion of Standards and Effectiveness of Land Use Planning Are Uncertain," GAO-RCED-94-144 (Washington, D.C.: U.S. General Accounting Office, August 1994), p. 5-6.]
5. Radionuclide Remediation Costs Are Highly Uncertain.
Failure to promulgate consistent limits on public exposure to radiation, or to answer the question of "How clean is clean enough?" by defining residual radionuclide levels in soil and water after cleanup, has delayed decisions about land reuse. Without the reassurance of consistently defined standards that will provide adequate protection to human health and the environment, affected parties have been understandably reticent to agree to land reuse decisions. Unfortunately, the range of possible land reuse choices and the degree to which each site will be cleaned up directly affect the amount of radioactive waste produced. Since the maintenance and safe storage costs of these radioactive wastes will require significant cost outlays far into the future, variation in the amount of radioactive waste accumulated for safe storage creates great uncertainty in the ultimate price tag for DOE's radionuclide cleanup challenge. The questions of acceptable radiation health limits, radionuclide standards for soil and water, and land use are thus integrally linked.
The need for a unified set of land reuse categories and related radionuclide cleanup standards for each reuse category that account for variation in naturally occurring background levels of radiation is urgent. DOE will shortly face a large wave of decisions for its cleanup actions, for which it will need information about radionuclide cleanup levels- According to a DOE analysis, approximately 100 preliminary or final restoration decisions will occur in 1996 and 1997. As noted in studies by the Office of Technology Assessment (OTA), NAS, and even DOE, unified cleanup standards for radioactive waste would accelerate cleanup efforts at DOE facilities. [David P. O'Very, The Regulation of Radioactive Pollution, pp. 294-295.] In summary, apparent delays in promulgating standards impede cost estimation, slow cleanup and prevent public land reuse decisions.
E. The Need to Develop and Implement More Cost-Effective Technology.
Environmental cleanup is currently limited by existing technology, as well as regulatory barriers and resistance to adopting new or unproven technology. Several pilot studies underway at various agencies employ new technologies that indicate significant potential for cost effectiveness. The potential long-term cost savings from the more rapid development of such innovative technologies may total in the billions. For example, the NPR concluded that innovative technologies could save up to 68 percent of the cost of cleanup using existing technologies. [National Performance Review Accompanying, Report, "Environmental Protection Agency," (Washington, D.C., September 1993), p. 25.] EPA, in a sample of 17 Records of Decision (RODS) using remedial technologies tested under the Superfund Innovative Technology Evaluation Program (SITE), projected an average cost savings of 62 percent for use of innovative treatment technologies over standard treatments. The total cost savings for the 17 RODs was projected to be $358 million. [Environmental Protection Agency, Superfund Innovative Technology Evaluation Program, Innovation Making, a Difference," EPA/540/F-94/505, (Washington, D.C.: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency), p. 4.] Extrapolating these projections to the entire cleanup program, and given that SITE has now demonstrated over 80 technologies, the potential savings are very substantial. DOE estimates that new techniques for cleaning up soils could potentially save as much as $2 billion at the Nevada Test Site and that new groundwater cleaning processes could save 3 billion. ["Congressional Budget Office, "Cleaning, Up the Department of Energy 's Nuclear Weapons Complex," (Washington, D.C., May 1994), pp. 73-7] Based on the level of ultimate land use at its sites, DOE's BEMR estimates technology can save between $10 billion and $80 billion from the program's total costs.
The early history of cleanup technology development was not nearly so bright. It yielded few results, despite the promising nature of many of the technologies under development. Participants in a "Workshop on Remediation Techniques" sponsored by OTA in 1990 agreed that there was little to show for the preceding ten years of Federal and private sector investment in cleanup technologies (with the exception of in situ vitrification and vapor vacuum extraction). [OTA, Complex Cleanup, pp. 70-71.] Even fairly recently, the General Accounting Office criticized DOE for "not having a well-coordinated and fully integrated technology development program. [GAO Report, "Department of Energy: Management Changes Needed to Expand Use of Innovative Cleanup Technologies," RCED-94-205 (Washington, D.C.: U.S. General Accounting Office, August 1994), p. 1.] The same GAO study concluded that there is inadequate coordination amongDOE's R&D organizations and programand project offices. [Ibid, p. 6.] While GAO recognized that DOE has begun to address this problem by formatting five priority focus areas for technology development based on the environmental cleanup program’s most pressing needs, it concluded that still further improvements could be made. [Ibid. pp. 6-7.]
The process for obtaining regulatory approval has at times hastened, and at other times slowed, the use of new technologies. The process can require input from regulators, site project mangers, local officials, and contractors. These various par-ties may have varying degrees of familiarity with the technology, distinctly different views on its acceptability, or different attitudes towards risk. Such differences can create problems in the methodology of technology selection and impede agencies from trying out new technologies. In addition, regulatory approval is hampered by a general lack of credible cost data for current and innovative technologies.
The uncertainty associated with the potential commercialization of new technologies also acts as a disincentive to private capital. Innovative technology companies often lack startup capital to complete the required field demonstrations, a necessary precursor to being awarded contracts of sufficient size to encourage further venture capital investment. As a result, few if any new remediation companies were formed in the last year. Even large firms indicate that the impediments to fast track development of innovative technologies have frequently been too cumbersome to yield the kind of attractive return on investment to warrant developmental funding.
It should also be recognized that there are real limitations to current cleanup technologies, which will, in some cases, require focus and the commitment of significant resources to solve. DOE's mixed waste tanks at Hanford, Washington, are an example of where limited technology exists to address the cleanup problem. In other cases, the technology exists but is extraordinarily expensive in relation to the benefits. Moreover, there are instances where the more commonly used technologies, such as incineration have become generally unpopular with local stakeholders. Some DOE cleanup problems, such as groundwater contamination, plutonium contamination of soil at Rocky Flats and Mound Plant, uranium processing residues in silos at Fernald, spent nuclear fuel and tanks containing high-level waste at Hanford, buried transuranic waste in Idaho, and mixed waste (hazardous and radioactive) throughout the complex present the most difficult technological challenges to solve in the years ahead. Long-range commitment of time and money to a coherent development of new technologies appears necessary if they are to be brought to the stage at which they can be applied to the problems left behind by weapons production.
V. The Path to Reform.
This survey of the current state of the Federal facilities cleanup effort identifies an agenda for reform in five areas, all of which are essential to enhancing the cleanup effort, improving efficiency in the deployment and use of available resources, and maintaining public acceptance and credibility. These areas are 1) statutory reform, 2) administrative and regulatory reform, management reform, 4) cost-effective technology development and implementation, and 5) budget process reform.
A. Principles of Reform
The efforts to address the many significant problems confronting Federal facility cleanup must be undertaken within a framework of principles that guide, inform, and constrain whatever reforms are needed to improve the efficiency and credibility of the cleanup effort. Extensive and productive discussions among Federal agencies, States, communities, and others have identified a number of the principles that should govern Federal facilities cleanups, and these are equally pertinent to the reform effort. For example, the Environmental Commissioners of the States (ECOS) and FFERDC convened by EPA, have developed two quite similar sets of consensus principles. After a process of review and synthesis, the FFPG has endorsed the following set of principles drawn from either the ECOS or FFERDC principles, with modifications indicated in italics.
1. State role. Under our Federal system of government, States have a primary responsibility to protect the environment, health, safety, and well-being of their citizens. Any legislative reforms should recognize this principle.
2. Federal role. The Federal government shares responsibility for protecting the environment, health, safety, and well-being of its citizens, as well as ensuring the appropriate use of Federal resources. This responsibility should not unduly impinge upon the role of states and should include the development of appropriate goals and standards for cleanup and provide resources for States that do not have sufficient capability or expertise to oversee complex facilities. As Part of its responsibility, the Federal government must honor its obligation to the citizens of this country to clean up its facilities, manage its wastes properly, and comply with environmental laws to the same extent as private parties.
3. Independent State regulatory oversight is necessary to achieve effective environmental results at Federal facilities. Duplicative oversight should, however, be avoided, and a lead regulator (Federal or State) should be designated whenever possible.
4. Negotiated compliance agreements and regulatory orders provide an effective framework for establishing priorities and reconciling competing interests. Agreements can and should be adapted to changed circumstances by renegotiating commitments, considering risk, technical, fiscal, and other appropriate factors.
5. Efficiency. While maintaining necessary health margins and public health protection, greater efficiency must be achieved in Federal and State environmental programs, especially in light of current and projected budget constraints.
6. Long-term commitments. A sustained national commitment to cleanup is required to assemble and maintain the resources and wise management necessary to address environmental needs at Federal facilities. In establishing this commitment, policy makers should consider that if important work is deferred, conditions may deteriorate and contamination may spread, increasing risks and the costs to address them.
7. Equity. Congress, Federal agencies, States, and the public must work together to establish treatment, long-term storage, and disposal sites for radioactive wastes and surplus fissile materials in an equitable manner.
8. Integrated planning and response. Integrated planning and response to all environmental obligations should be encouraged, in order to address significant site priorities in a sensible, efficient manner.
9. Public Participation. The adverse impacts of Federal facilities have fallen most heavily on their neighbors. Affected public stakeholders must have meaningful involvement in Federal facility environmental decisions.
10. Environmental Justice. The Federal government has an obligation to make special efforts to identify and address risks related to Federal facility activities in low-income and minority communities that have been disproportionately and adversely affected by exposure to environmental risks. Federal agencies must incorporate the principles of environmental justice, as set forth in Executive Order 12898 (Feb. 24, 1994), into every phase of the cleanup process.
11. The importance of pollution prevention and pollution control activities. Effective pollution prevention and pollution control activities are essential to prevent future environmental cleanup problems. Therefore, in carrying out their mission, Federal agencies should view such activities as a cost of doing business and fully comply with environmental laws and regulations that are designed to accomplish these objectives.
12. The role of future land use determinations in making cleanup decisions. Reasonably anticipated future land uses should be considered when making cleanup decisions of Federal facilities, provided that at the time of any land transfer there are adequate safeguards to protect land holders, those who will receive or lease the land, and surrounding committees. The communities that are affected by Federal facility cleanups, along with their local governing bodies and affected Indian Tribes, should be given a significant role in determining reasonably anticipated future use of Federal property that is expected to be transferred, and in how future use determinations will be used in making cleanup decisions.
13. Cleanup contracting. Federal facility environmental cleanup contracts should be managed as efficiently as possible by using contract mechanisms that specify, measure and reward desired outcomes and efficiencies rather than simply reimburse for effort or pay for an end product. Federal agencies should strive to ensure that cleanup contracts and employment opportunities benefit local communities, particularly those that are lacking economic resources and have been disadvantaged by contamination. Contractors and agencies responsible for cleanup should work in partnership with local communities to achieve cleanup goals.
14. Consideration of human health risk and other factors in Federal facility environmental cleanup decision making. Human health is an important and well established factor that should continue to be a primary consideration in Federal facility cleanup decision making, including setting, environmental cleanup priorities and enforceable milestones. However:
a) Risk assessment and other analytical tools used to evaluate risks to human health (including non-cancer as well as cancer health effects) all have scientific limitations and require assumptions in their development. As decision aiding tools, risk assessments should only be used in a manner that recognizes those limitations and assumptions. Moreover, risk assessments ought not be used by any party as a basis for unilaterally setting aside legal requirements that embody public health principles and other important societal values.
b) In addition to human health risk, other factors that warrant
consideration include:
short-term and long-term ecological efforts and environmental impacts in general, including damage to natural resources and lost use;
making land available for other uses;
acceptability of the action to regulators, tribes, and public stakeholders;
statutory requirements and legal agreements;
life cycle costs;
pragmatic considerations, such as the ability to execute cleanup projects in a given year, and the feasibility of carrying out the activity in relation to other activities at the facility; and
overall cost and effectiveness of a proposed activity.
Fiscal constraints do not justify a failure to take actions to protect human health and environment, but may result in a need to set priorities about the timing of cleanup actions.
15. The need for a systematic approach to decision making and priority setting. Federal facility priority setting decisions should be made in a manner that recognizes their interconnectedness to other environmental problems.
16. The role of studies in the cleanup process. The identification and characterization of contamination and the evaluation of health impacts on human populations are essential parts of the cleanup process. Efforts to streamline the cleanup process should focus on reducing paperwork and moving away from adversarial relations toward cooperation, not the arbitrary capping of funding for studies.
B. Statutory Reform.
1. Superfund Reauthorization.
In the 103rd Congress, the Clinton Administration developed a comprehensive set of reforms to CERCLA that had broad bipartisan support and closely followed the principles described above. The Administration's bill, H.R. 3800, attracted the support of a broad coalition of groups concerned about the Superfund program, ranging from environmental and community groups to States and industry. Despite this support, legislation reauthorizing the Superfund program was not passed. While the current Congress has not yet developed any proposals with similarly broad support, the Administration will continue to advocate responsible reforms to CERCLA and to support statutory changes that conform to the principles recited here and reflected in last year's bill.
As in other Federal environmental legislation, this bill reaffirmed the mandate that Federal agencies comply with the environmental laws to the same extent as private entities, and preserved the liability of Federal facilities for natural resource damages. But the relief the bill's reforms provided to responsible parties -- both public and private -- had particular importance to Federal facilities.
The most significant of the changes advocated by the Administration were those in remedy selection. The proposed reforms would have established a more efficient remedial decision process and more cost-effective remedy selection criteria, while continuing to require protective and reliable remedies. Under the Administration's approach, risk assessments were made more realistic and the role of costs was elevated. Cleanup levels were set according to the reasonably anticipated future land use at the facility, ensuring a better correlation of cleanup costs and actual cleanup benefits. This reform alone promises significant savings at sites ranging from DOE nuclear weapons facilities, where huge expanses of land may be unusable for the foreseeable future, to DOI and USDA mining sites that are remote from any human habitation. The current statutory preference for permanence and treatment in remedy selection was limited to principal threats or "hot spots," promising additional and significant reductions in the cost of cleanup. The bill reformed the ARARs process by establishing a more rational process for determining "applicable" State laws, and by eliminating from CERCLA "relevant and appropriate requirements" that are not otherwise applied by States to remediation. The bill also encouraged greater use of presumptive remedies and innovative technologies, while reforming the standards governing groundwater cleanup to reduce unnecessary cost. OMB determined that, taken together, these remedy selection reforms could save 20 percent or more of the cost of cleaning up Federal facility sites on the NPL.
There were also a number of provisions in the bill that would have afforded significant relief to USDA and DOI at mining sites requiring cleanup. A new section of the law would have promoted remining, by providing liability protection to those mining operations that had nothing to do with the release of hazardous substances or disposal of hazardous waste, but whose operations could significantly reduce the ultimate costs of cleanup. Other provisions would have ensured that responsible parties would be brought in early to address contamination on Federal lands, rather than requiring the land management agency to automatically treat contaminated sites caused by private mining as a Federal facility.
The bill's provisions for State role would have minimized duplicative oversight and, through a program of delegation of regulatory authority at NPL sites to qualified State programs, would have eliminated the major source of redundancy and contention concerning Federal and State roles in the cleanup process. States with corrective action authority under RCRA, comprising more than half the States, would automatically have had the option of assuming EPA's CERCLA authorities at Federal facilities.
The Administration recognized that public acceptance of cleanup standards permitting such significant cost savings would require enhanced public participation in the cleanup process, so that affected communities could have a voice in such fundamental decisions as a site's future land use at a site. Consequently, the bill included expanded and enforceable community participation requirements. These requirements reflected Federal agency leadership in developing effective mechanisms for community participation in the cleanup process, as they were modeled in part on the RABs and SSABs now utilized by DOD and DOE, respectively. There was also recognition that the proposed reforms had to be applied with greater care in those communities that might be subject to multiple risks from a variety of sources, such as low income and minority communities that suffered disproportionate and adverse exposure to environmental risks.
While the prospects of Superfund reform in this session of Congress appear remote, reforms like those described here are the fundamental building blocks of any effort to reform the Superfund program without diminishing of human health and the environment. They are also fundamental elements of any effort to reduce the costs of Federal facility cleanups under Superfund. The Administration will continue to press for these and other elements of its CERCLA reform agenda in any legislation that is proposed.
2. RCRA Reform.
As part of a broader National Performance Review process of "Reinventing Environmental Regulation," the Administration announced in early March 1995 that it would convene a series of stakeholder discussions intended to develop a narrow set of targeted reforms to RCRA that would eliminate or modify requirements that generate high costs and only marginal environmental benefit. [Environmental Protection Agency, "Reinventing Environmental Regulation," (Washington, D.C.): Environmental Protection Agency, March 16, 1995] As in the case of CERCLA, any proposed reforms would apply equally to responsible parties in the public and private sector, but the reforms discussed in the stakeholder process clearly would provide significant relief to Federal facilities.
For example, there was general agreement among those participating in the process that RCRA treatment of contaminated media should be reformed, either through legislation or regulation, so that standards promulgated for high-risk industrial wastes will not govern low-risk cleanup wastes. There was also significant attention to proposals to improve integration of RCRA with other environmental statutes, to expand the circumstances under which EPA could rely on management standards in lieu of RCRA regulation, and proposals to provide general permitting of identical facilities. All of these proposals have the potential to provide significant cost savings for Federal facilities.
C. Administrative and Regulatory Reform.
Soon after the 103rd Congress adjourned without enacting the Administration's Superfund reform bill, EPA announced a series of reforms to begin implementing as many of the proposals in the bill as current law permits. Where appropriate, EPA has sought corresponding reforms to RCRA. These reform efforts by EPA are ongoing and are assuming more importance for Federal facilities as the prospects for Superfund reform in this calendar year become increasingly uncertain.
1. Future Land Use and Remedy Selection.
For Federal facilities, the most significant of EPA's administrative reform efforts to date has been the development of a guidance, issued in May 1995, that explicitly links remedial decisionmaking with the reasonably anticipated future land use at a site. This reform will yield significant time and cost savings at the many Federal facility sites where inappropriate land use decisions could lead to inordinately costly remedies bearing no relationship to actual risks. Consistent with the Administration's overarching principles of community participation in, and acceptance of, remedial decisions, the guidance explicitly requires consideration of the views of the local community in making future land use determinations.
Previously, future land use was not uniformly considered in developing comprehensive cleanup strategies for Federal facilities, even though it may be the single most important determinant of cleanup costs. Indeed, alternative land use scenarios (under current law and using existing technologies) can affect the estimated cost of cleanup as much as twofold. [U.S. Department of Energy, Estimating The Cold War Mortgage , The 1995 Baseline Environmental Management Report, p. 44.] An example from DOE highlights the significance and potential savings for Federal facilities associated with EPA's reform. At Fernald, the future land use initially projected by remedial planners included potential use of the site as a residential and agricultural area, requiring that large quantities of soil be removed and disposed of off-site. The Fernald Citizens Advisory Group evaluated alternative land use options, including industrial and recreational uses. The group ultimately recommended land uses with fewer potential pathways for human exposure to contamination. This allowed cleanup plans to include less removal of contaminated soil, even as the prime sources of groundwater contamination were removed. This reduced the life-cycle cleanup costs by approximately $1 billion. [Ibid.]
2. Better Consideration of Cost and Risk Issues.
Future land use guidance is an important example of EPA's recent leadership in ensuring that CERCLA's statutory criteria are not implemented in a manner that yields costly remedies with no commensurate benefits for public health and the environment. It is also an illustration of EPA's effort to develop management and decisionmaking tools to ensure that remedial decisions give appropriate consideration to cost-effectiveness and the relative benefits of their cleanup choices, and to do so without saddling the cleanup process with unwieldy analytical requirements.
Consistent with this approach, and to provide both transparency and discipline to the role of cost in cleanup decisionmaking EPA and other Federal agencies have agreed to develop a standard format for a concise summary of site risks, the costs of cleanup alternatives, the relative cost-effectiveness of cleanup alternatives, and the anticipated benefits of each cleanup alternative. Once developed, this summary would be required for major cleanup decisions at both Federal and non-Federal facilities. In these summaries, the discussion of costs and identification of benefits would incorporate the methodology and limitations of Executive Order 12866: statutory standards would not be changed; benefits could be described qualitatively rather than quantitatively; and unquantifiable benefits related to significant policy concerns (such as community preferences, natural resource damage concerns, State policies, or environmental justice) could be invoked to justify more protective cleanup levels and more costly cleanup alternatives. As this summary is developed, agencies will be exploring ways in which a more expanded use of site-specific cost-effectiveness analysis could be undertaken at facilities without unduly slowing the pace of cleanup.
To ensure that this mechanism yields more attention to the role of cost and greater consistency in cleanup decision making, EPA is bolstering this approach with additional guidance to its regions. EPA will issue new directives: 1) requiring consistency in application of national policies, especially with respect to consideration of future land use, groundwater, and presumptive remedies; 2) highlighting the role of cost and cost-effectiveness in remedy selection, making clear that cost-effectiveness is a screening mechanism in selecting remedies and that inordinately costly remedies are to be avoided; and 3) acknowledging that the statutory mandate for establishing that cost-effectiveness is on an equal footing with the mandate to use permanence and treatment to the maximum extent practicable, in selecting remedies.
Concurrently, EPA is working with Federal agencies on a cooperative basis to develop management tools that provide better implementation of these directives. EPA is committed to the development of cost effectiveness measures or "rules of thumb" that will provide objective criteria for identifying and providing closer scrutiny of inordinately costly cleanup choices. EPA is also working with other Federal agencies to ensure that the risk analysis and any risk summary takes into account any significant or unusual risks to workers or to natural resources that may be attributable to cleanup activity. Thus, where risk to cleanup workers dealing, with highly radioactive waste may far exceed the risk reduction associated with a cleanup alternative, that information will be available to the cleanup decision makers. Similarly, when a cleanup activity may itself injure natural resources. that information will also be taken into account, so that all environmental risks are evaluated when weighing alternatives.
3. Streamlining Standards and Reducing Redundancy.
While the current overlap of CERCLA response and RCRA corrective action authorities may not be fully eliminated in the absence of legislation, EPA and DOE are working cooperatively to ensure that standards in the two programs are integrated as much as possible. EPA currently plans to promote greater parity between the two programs through a new RCRA/CERCLA integration guidance. DOE, in coordination with EPA, is developing a similar guidance tailored to the EM program. EPA also plans to issue an advanced notice of a proposed rulemaking (ANPRM) to make RCRA regulations as consistent as possible with CERCLA policy on considering future land use. In addition, EPA has initiated an effort to identify Federal facility sites at closing bases where, consistent with DOE's policy for non-Federal-facility sites, NPL listing may be deferred based on certain criteria, including State qualifications.
There are a number of other opportunities in which EPA, in consultation with affected Federal agencies, plans to increase flexibility, encourage consistency, and reduce the costs of its cleanup programs. Through the Hazardous Waste Identification Rule (HWIR) rule for media, EPA could establish broad exemption standards for low-risk contaminated media, as well as an expedited permitting process and more flexible management standards for higher-toxicity media. In a forthcoming HWIR rule for process waste, EPA could consider higher residual standards for disposal at facilities regulated by the AEA. Any of these changes could generate significant cost savings at DOD and DOE facilities.
In addition, beginning with an ANPRM scheduled for September 1995, fundamental changes to the corrective action under RCRA will be pursued. These changes will be intended to ensure protective standards while reducing cost, minimizing regulatory "command and control," increasing consistency, and reducing compartmentalization. EPA's goal is to incorporate proposed legislative, regulatory, and administrative reforms to CERCLA to the maximum extent permitted by statute and to encourage use of the ANPRM as a guidance while the rulemaking is pending.
Of particular significance for DOE, EPA also plans to complete, in this calendar year, several actions to resolve issues surrounding radiological waste cleanup. Specifically, EPA plans to publish much needed cleanup standards on radionuclides, removing a substantial source of uncertainty for many DOE cleanups. The absence of these standards and guidance now generates enormous uncertainty for DOE.
While the preceding reforms are directed in equal measure to responsible parties in both the public and private sectors, EPA is striving to improve communication among Federal facility agencies and both their State and Federal regulators. For its part, EPA has begun a series of regular meetings with Federal agencies to identify and address, on a timely basis, disagreements on cleanup issues. This process should improve the remedy selection process. As part of this effort, EPA is engaging in greater consultation with Federal facilities on each of its implementation plans for administrative reforms.
4. Better Risk Judgments and Risk-based Priorities.
The National Academy of Sciences report [National Academy of Sciences, Building Consensus through Risk Assessment and Management of the Department of Energy's Environmental Remediation Program (Washington, D.C.: National Academy of Sciences, January 1994).] endorsing greater use of risk-based decisionmaking and DOE's consequent development of risk principles adhering to those developed through an interagency process led by OSTP, promises significant and continuing improvement in the quality of risk analysis, with corresponding gains in the soundness of remedial decisions. This effort will be supported by joint work among EPA, DOE, and DOD on risk assessment and risk characterization, in part through implementation of Administrator Browner's risk characterization guidance of March 1995. The series of reforms now planned or completed by EPA, including policy directives like its future land use guidance, each promise better use of risk information and more realistic risk assumptions.
These improvements will help facilitate more extensive use of risk-based priority-setting among Federal agencies, helping to assure the optimal use of increasingly limited Federal resources for Federal facilities cleanup. DOD and DOE are both using the three-tier categorization of site activities described in Chapter 4, in which site activities are identified according to whether they address low, medium, or high risk. Both departments are in the process of setting priorities among the facilities in their portfolio and among specific remedial activities across sites. Initial work has tended to confirm that budgetary resources are primarily devoted to the highest-risk sites, [U.S. Department of Energy , Risks and the Risk Debate: Searching for Common Ground, "The First Step" Draft, p. ES8.] but there remains significant room for improvement.
5. IAG Initiatives.
Reforms that lead to better risk information and that identify risk-based priorities provide the requisite management tools and information for better deployment of limited Federal cleanup resources, but there is a need to better translate these priorities into achievable and enforceable milestones in agreements.
The analysis in Chapter 4 describes circumstances that led to the negotiation of some IAGs with milestones that may need to be revised in light of improved information about sites, better understanding about risks and priorities, and unanticipated changes in appropriated funds. Federal agencies and Federal and State regulators must work together to more effectively resolve priority-setting issues. Decisionsmay result in funds being shifted, in the short term, from one site to another presenting greater risks. There must be continued willingness to exercise forbearance in enforcement where a milestone cannot be met due to lack of appropriated funding and to make maximum use of the flexibility available in the IAG process for revising milestones.
In order for Federal agencies to approach the IAG issue in the spirit of the reform principles presented here, and for Federal and State regulators to consider these issues in a cooperative and constructive spirit, a number of principles for the IAG process should be articulated:
Federal agency risk-based priority setting will serve as a primary point of departure in setting milestones in the IAGS;
Milestones should be readjusted on the basis of the expected availability of new technology, newly discovered site conditions, and Congressional funding decisions;
Regulators will be routinely involved in site-wide planning;
Regulators will be routinely involved in identifying, implementing, and monitoring productivity improvements;
Stakeholders will be afforded routine opportunities to participate in the cleanup and priority-setting process;
Local stakeholders will be consulted in the development and application of site- specific, risk-based priority setting; and
Federal agencies will make up funding shortfalls from reasonable efficiency/ productivity sources before asking for changes to milestones.
Ideally, a dialogue between Federal facilities and their Federal and State regulators according to these principles will foster acceptance of IAG and milestone modifications. Any such modifications should implement a cleanup strategy to address the most urgent sites first and then: (1) clean up what is technically straight forward or "easy"; (2) stabilize what cannot be cleaned up in the near term; (3) prioritize cleanup based on risk and availability of technical solutions; and (4) focus on what will get land back into public use and reduce overhead costs.
6. Promoting Economic Redevelopment.
In each of the proposed statutory and administrative reforms initiated by the Administration, the need to promote economic and environmental redevelopment at contaminated or formerly contaminated sites has assumed a high priority, as exemplified by EPA's Brownfields Action Agenda for Superfund sites. This policy is fully applicable to Federal facilities. The fast-track process for base closure, discussed in Chapter 3, is an important element of this goal at closing DOD bases. Liability protection for prospective purchasers, as set forth in last year's Superfund bill, would reinforce this goal. A number of further reforms, not reflected in the Administration's Superfund bill, may be necessary to ensure that environmental cleanup does not impede economic redevelopment of Federal facility sites. Specifically, clearer authority for DOD to transfer property before cleanup action is completed, either by lease or transfer, and better standards to define those facilities subject to limitations on transfer, would enhance DOD's ability to expedite, and deploy nonfederal resources to, cleanup of closing bases.
D. Management Reform.
DOE has budgeted 20 percent in management savings to be realized through efficiency gains, in addition to the already substantial efficiency gains that have been achieved by eliminating historic inefficiencies. Further and dramatic reforms in the areas of contracting methods and management, and the internal management of the agency, are necessary. Some of these initiatives may prove useful for cleanup programs in other departments. Other management initiatives that would improve the cleanup process include: improving information systems to help program managers do better strategic planning, budgeting and oversight; improving strategic planning and oversight at agency headquarters; and moving to privatize whenever cost-effective.
As an integral part of its Reinventing Government (REGO) strategy, DOE plans to achieve $4.4 billion in outlay savings from the Environmental; Management (EM) program over the next five years, FY 1996 to FY 2000. This savings commitment is very aggressive and will require substantial changes to the way the EM program is run. The Department is considering a comprehensive and far-reaching set of initiatives, including but not limited to efficiency and productivity improvements, to achieving these savings. The measures include:
1. Contract reforms, contract management oversight and other internal management reforms.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E. Cost-Effective Technology Development and Implementation.
A wealth of promising research and development is being done in Federal, academic and business circles within the area of remediation technology. Historically, however, there has been a marked lack of emphasis on bringing innovative environmental technologies into widespread use in a cost-effective manner. Over the past two years, the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) undertook the task of defining the goals of a national environmental technology strategy which culminated in publication of the April 1995 report, Bridge to a Sustainable Future. [National Science and Technologies Council, Bridge to a Sustainable Future: A National Environmental Technology Strategy, (Washington, D.C.: National Science and Technologies Council, April 1995), p. i-vi.] This study looks primarily at the national impact of innovative pollution prevention, environmental compliance, and remediation technologies, perhaps the greatest benefits may eventually accrue to the Federal facility cleanup effort. This would require adaptation of the national strategy to the specifics of Federal facility cleanup. Federal agencies have made significant progress toward this goal through rapid development, cross-fertilization, and eventual fast track implementation of the most promising and most needed cleanup technologies.
1. Some Innovative Cost-Effective Technologies Are Reaching Profitable Commercialization.
DOD and DOE have experimented on a limited scale with a number of new technologies and have some of the best preliminary results. DOD, which has used such techniques as bioventing and bioremediation to reduce costs, has several technology initiatives underway. Under auspices of the Naval Environmental Leadership Program, the Navy is implementing a cone penetrometer test at Naval Air Station North Island, California. This technology is being used to characterize the extent of the contamination at an industrial treatment plant. Without this technology, the Navy would not have been able to characterize the site adequately because conventional drilling and sampling techniques would not obtain complete subsurface stratigraphic information. [Department of Defense, Defense Environmental Restoration Program: Annual Report to Congress for Fiscal Year 1994, pp. 31-32.] Another site demonstration in progress is the joint effort of a consortium of six companies -- DuPont, Dow, General Electric (GE), Monsanto, Zeneca, and Ciba-Gigy -- along with EPA, the academic community, and the Air Force to develop in-situ bioremediation technologies to degrade chlorinated solvents in soil and groundwater at Dover Air Force Base. This collaborative effort between the Federal government, industry, and academia, which evolved from a Work Group of the Remediation Technologies Development Forum (RTDF), biodegrades chlorinated solvents (TCES) in place by pumping oxygen into the contaminated zones to facilitate cometabolic destruction at a fraction of the cost to unearth and neutralize the solvents.
DOE has developed effective new technologies for some of its more conventional contamination problems. Vapor vacuum extraction, a process whereby volatile organic contaminants are extracted from soil by pumping and auctioning shallow underground wells, has been successfully tested at Savannah River and Idaho National Engineering Laboratory. Another RTDF technology, Lasagna developed through a consortium of Monsanto, E.I. DuPont de Nemours & Co., Inc. (DuPont) and GE, with participation from EPA and DOE, and facilitated by Clean Sites, Inc. under a cooperative agreement with EPA's Technology Innovation Office, is already entering the site demonstration phase at the DOE Gaseous Diffusion Plant in Paducah, Kentucky. In this technology, electro-osmosis is combined with treatment zones (sorbents, catalytic agents, microbes, oxidents, etc.) created by hydrofracturing or pneumatic fracturing of the soil to electrically force migration of water to flush contaminants from the soil into the treatment zones for stabilization or removal.
Some DOE cleanup problems, such as groundwater contamination, plutonium contamination of soil at Rocky Flats and Mound Plant, uranium processing residues in silos at Fernald, tanks containing high-level waste at Hanford, and buried transuranic waste in Idaho, will be the most difficult technological challenges to solve in the years ahead. Since the radiological half-lives of many of DOE's wastes are measured in years, centuries or millennia, new cleanup technologies for DOE must focus on stabilizing the waste for timeframes so far into the future that assessing the new technology's effectiveness becomes much more problematic. Long-range commitment of time and money todevelopment of new technologies appears necessary if they are to be brought to the stage at which they can be applied to the problems left behind by weapons production.
2. Cost-Effective "Green" Technologies on the Horizon.
There are many more technologies which have yet to be tried on any significant scale, but which bear close examination. One particularly intriguing new technology, called phytoremediation, uses green plants for removing or degrading pollutants in the environment. Techniques to use bacteria and algae to remediate contaminants have been under development for some time. However, new research into terrestrial plants has demonstrated that some of these plants concentrate chemicals and metals (both heavy and radioactive) in their root systems, in levels far exceeding those in surrounding soils and waters. Various species of plants have varying degrees of effectiveness in selectively removing different types of chemicals, radionuclides, or heavy metals from soils and waters. Plants able to accumulate most heavy metals have been identified. Phytoremediation of metals comprises three technologies (i) phytoextraction, in which metal-accumulating plants are used to transport and concentrate metals from the soil into the harvestable parts of roots and above-ground shoots, (ii) rhizofiltration, in which plant roots absorb, precipitate and concentrate toxic metals from polluted effluents, and (iii) phytostabilization, in which metal tolerant plants are used to immobilize metals in soils, thereby reducing their environmental risk. [Ilya Raskin, 14th Annual Symposium Abstract Book: Current Topics in Plant Biochemistry, Physiology and Molecular Biology; Rhizofiltration - using plants for remediation of heavy metals in water (Columbia, MO: University of Missouri-Columbia, April 1995), p. 61.] In some cases, it has even been possible to remediate mixtures of heavy metal and chemical pollutants simultaneously. Time, however, is the tradeoff. Contamination is removed by successive growing and harvesting of terrestrial plants in order to phytoremediate contaminated soils to acceptable levels. [Burt D. Ensley, 14th Annual Symposium Abstract Book: Current Topics in Plant Biochemistry, Physiology and Molecular Biology; Will plants have a role in bioremediation? (Columbia, MO: University of Missouri-Columbia, April 1995), p. 2.] The harvested vegetation, rich in accumulated contaminants, is then fairly easily and safely processed by reducing to ash to remove the contaminants -- even in the case of radionuclides. The volume of waste is generally a fraction of that of many current, more invasive remediation techniques and the associated costs several magnitudes less.
There are ancillary benefits of this and other "green" technologies. Reclamation of some metals may be made from plant ash resulting from phytoremediation, which reduces generation of new heavy metal waste and generates recycling revenues. [Rufus L. Chaney and J. Scott Anale, "Green Remediation": Potential Use of Hyperaccumulator Plant Species to Phytoremediate Soils Polluted with Zinc and/or Cadmium, The Revival Field Project, (Beltsville, MD: USDA Agricultural Research Service and University of Maryland).] More distantly on the horizon, it may be possible to combine bioengineering and phytoremediation technologies to develop crops for feed that will prevent the accumulation of pollutants and toxins through the food cycle. This discussion is meant to highlight just one of many types of innovative technologies applicable to Federal facility cleanup that is both cost-effective and in keeping with the strategic vision to encourage environmentaltechnologies for a sustainable future. Adding the USDA to the Federal Remediation Technologies Roundtable (FRTR) would help elevate the profile of these green technologies and bring a new set of experts into the information sharing process.
3. A Strategic Vision for Federal Facility Cleanup Technology Development.
It is a widely accepted belief that proper investment in the nation's technological base for nuclear and hazardous waste management will ultimately lead to greater efficiency and cost reduction in the cleanup of Federal facilities. [OTA, Complex Cleanup, p. 68.] The framework for action developed in the reports, Technology for a Sustainable Future and Bridge to a Sustainable Future, serve as the primary blueprint for defining a more specific strategic vision for Federal facility cleanup. Particularly useful recommendations from these reports, many of which agencies have begun applying to their Federal cleanup programs, are:
Develop a new generation of incentive-based policies and programs stressing performance, flexibility, and accountability, [National Science and Technology Council, Technology for a Sustainable Future: A Framework for Action, pp. 2-28.]
Create better frameworks to share and coordinate information among developers;
Promote formation of organizations or consortia that promote collaborative technology development;
Develop methodology to achieve fast-track regulatory approval for promising technologies;
Help create a positive climate for venture capital funding through encouragement of interstate regulatory reciprocity and streamlined permitting and technology verification; and
Create a "one-stop-shop" to assist firms, especially small innovative technology companies, to confront the maze of complex organizational structures and Federal "information jungle".
Efforts like those taken at DOE in creating a new management system for its technology development program are significant steps in adopting the "Sustainable Future" strategic vision to the problems of Federal cleanup. DOE's new system for technology development designates five priorities or "focus areas;" 1) mixed waste characterization, treatment, and disposal, 2) radioactive tank waste remediation, 3) contaminant plume containment and remediation, 4) landfill stabilization, and 5) facility transitioning, decommissioning, and final disposition.
The program also pursues crosscutting and supporting technology areas such as characterization, efficient separations and processing, robotics, and technology transfer. DOE's focus areas provide forstronger ties between technology developers and environmental management users, as well as stakeholders. DOE has identified a site champion for each focus area and provides those sites the resources to implement the program throughout the nuclear weapons complex. The focus area concept enables more effective use of DOE-wide environmental research and technology development, including National Laboratories, to build on successive demonstrations of technologies. This site-lead structure also tries to give sites incentives to pursue technology demonstrations at their site, overcoming typical site and regulator hesitation at being the first to demonstrate a technology, thus taking on the greatest risk for failure.
To guide its technology development decisions, DOE now uses a Technology Investment Decision Model to track technology maturation: from basic and applied research, through exploratory, advanced, and engineering development, to demonstration and implementation. DOE has developed decision criteria to guide decisions at each of these stages. The stages include response to user-defined problems, success at solving the problems for which they are being developed, protection of user/public safety and health, commercial market potential, public/ stakeholder acceptance, regulatory acceptance, and legal protection of intellectual property rights.
Other agencies are implementing similar programmatic reforms that adapt national environmental strategy to their Federal cleanup challenge. Better allocation of scarce R&D funding should result. Roundtable discussions, similar to the December 1994 White House Conference for all environmental technologies, could be held regularly to guide development of innovative remediation technologies. Led by the National Science Technology Council (NSTC), the progress of groups like the FRTR and RTDF could be both elevated and coordinated to ensure inter-departmental synergy is maximized via a cohesive strategy. Between semi-annual discussions, the efficient sharing of innovative technology information among agencies and other stakeholders through roundtables like the FRTR can maintain the cross-fertilization of ideas and the link between agencies' technology strategies.
4. Fast-track Development of New Technologies.
The process for obtaining regulatory approval can hasten or slow the use of new technologies. The process can require input from regulators, site project managers, local officials, and contractors. These various parties may have varying familiarity with the technology, distinctly different views on its acceptability, or different attitudes towards risk. The NPR recommended that EPA develop an action plan for improving the regulatory and statutory climate for innovative technologies. [Op. cit.]
One effort in this area has been undertaken jointly by Federal agencies and States in the Western Governors Association Interstate Technology and Regulatory Cooperation (ITRC) Work Group. This group is developing test and demonstration protocols for interstate acceptance of the results of innovative technologies. This approach would leverage the scarce dollars available for demonstration of innovative technologies by allowing the results to be acceptable to a number of States besides the one hosting the demonstration. A recently signed Memorandum of Understanding among California, Massachusetts, Illinois, and New Jersey represents a major step toward interstate cooperation. Agencies working together will move down the learning curve for a given technology much more rapidly. The hoped-for result will be a dramatic reduction of Federal costs for proving and implementing innovative cleanup technologies.
5. Coordination of New Technologies.
Better information sharing and coordination among developers, users, regulators, and other stakeholders will share agency successes between sites and agencies, while also avoiding repetitive learning of non-successes. Putting collaborative technology development on the critical path for particular site cleanups can accelerate technology development and implementation, especially with significant stakeholder involvement in planning and oversight. Recognizing this, DOE has recently asked the National Academy of Science to perform two reviews, to be completed by the end of 1995. The first review focuses just on technology development, and the second more broadly evaluates the science, engineering, and technology bases for DOE's environmental management program. Both of these efforts are intended to identify obstacles to the program's success and make recommendations for the program's next steps.
Several interagency groups have been formed to foster communication among Federal agencies and the public on innovative technologies, including:
Environmental Technology Working Group is the primary interface among Federal agencies. Part of the NSTC, this group is chaired by the OSTP, with co- chairs by DOE and the National Science Foundation. Its purpose is to implement the National Environmental Technology Strategy.
Interagency Environmental Technology Office helps implement responsibilities assigned by the Environmental Technology Working Group and facilitates cooperative agency ventures and partnerships.
Federal Remediation Technology Roundtable is comprised of EPA, DOD, DOI, DOE, and the NCR.
Remedial Technologies Development Forum is a consortium of partners from industry, Government (DOD, Air Force, Army, DOE, EPA) and academia.
Environmental Security Technology Certification Program exists between DOD and DOE.
Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP) consists of EPA, DOD, and DOE representatives.
Demonstration of Onsite Innovative Technology (DOIT) program is a joint initiative among the Western Governors Association, EPA, DOD, DOE and DOI. Their mission is to more cooperatively develop innovative remedial solutions between States, commercial entities, and the Federal government.
Rapid Commercialization Initiative, sponsored by DOC, DOD, DOE, EPA, Southern States Energy Board, Western Governors Association, and the California Environmental Protection Agency, attempts to reduce barriers impeding market entry into technologies of strategic importance.
In addition, individual agencies have created their own formal mechanisms to bring environmental professionals together to share experiences, exchange information and establish cooperative efforts. For example, EPA has created both the National Advisory Committee for Environmental Policy and Technology and the Bioremediation Action Committee. EPA has also developed systems to assemble, maintain, and disseminate data on innovative technologies, such as its GIS/Key TM Environmental Data Management System and Vendor Information System for Innovative Treatment Technologies. Agencies also coordinate with private industry on mutual cleanup concerns. For example, DOE has partnered with both Dow and DuPont chemical companies in developing bioremediation systems and silicon barriers.
Communication and coordination within agencies is also important. A recent GAO study concluded there is not adequate coordination among DOE's R&D organizations and program and project offices. [GAO Report, "Department of Energy: Management Chances Needed to Expand Use of Innovative Cleanup Technologies," August 1994.] While GAO recognized that DOE has begun to address this problem by formatting five priority focus areas for technology development based on the environmental cleanup program's most pressing needs, it still concluded that further improvements could be made. [Ibid, pp. 6-7] Two extant assists are EPA's Cleanup Information Bulletin Board System (CLU-IN) and the Alternative Treatment Technology Information Center (ATTIC), electronic information clearinghouses on innovative treatment technologies, which can foster both intra-agency as well as interagency knowledge sharing.
Joint testing is another important element of technology coordination. Importantly, many of the most promising and rapidly commercialized innovative technologies have been the result of such joint interagency testing. The in-situ bioremediation technology program at Dover Air Force Base, mentionedearlier in this section, exemplifies how joint testing can accelerate movement of all departmental programs down the remediation technology learning curve. Another is a recent Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) at McClellan Air Force Base in California, which created a partnership among the Air Force, EPA, the State and several private companies to test new technologies for solvent remediation. These initiatives, as well as the Superfund Innovative Technology Evaluation, DOIT, and National Environmental Test Site programs, highlight the Federal government’s commitment to finding and using Federal facilities to jointly test technologies.
F. Budget Process Reform
As Federal resources to meet all national needs become more constrained, public awareness of the important contribution made by the Federal budget process in setting priorities for Federal facilities cleanup and in governing the pace of their accomplishment has grown. Along with self-imposed mandates for continuing program improvement, national fiscal conditions are forcing agencies to prioritize their cleanup efforts within and across sites according to better evaluation of alternative future land uses, estimates of risk, evaluations of available technologies, and analyses of the relative costs and benefits of alternative approaches to cleanup. Negotiated cleanup agreements should continue to play an important role in the Federal agency cleanup program, but more flexible agreement structures are needed to help ensure that limited resources are used as wisely as possible. In order to ensure that the limited Federal resources available to protect public health and safety and the environment are used as wisely as possible, agreements should recognize the need to address the most urgent risks first, incorporate these more rigorous methods of establishing cleanup priorities, and be capable of ready adaptation to new information, budget constraints, and changing circumstances. These kinds of negotiations will obviously be difficult, but they are critical if the Nation is to come to grips with the dilemma posed by limited resources and the extraordinary costs of addressing this problem.
In addition, the Federal budget process should continue to pressure agencies to implement management reforms that will reduce costs of operations. For example, cost savings include: speeding the adoption of cost-saving technologies, using more cost-effective contracting methods, adopting best practices from other agencies and the private sector, streamlining management structures and processes, and eliminating unnecessary overhead. Systematic introduction and evaluation of performance measures in the budget process can facilitate accomplishment of this goal.
More stable funding of Federal agency cleanup programs can help ensure that cost effective cleanup programs focused on risk reduction are implemented. When funding levels vary widely from year to year, Federal agencies cannot conduct efficient efforts that maximize the taxpayers' return on investment. Finally, if the process is to work, all stakeholders must be informed about and have meaningful opportunity for input into key decision-making processes.
VI. Conclusion.
The Federal government is making progress and improvement in environmental cleanup and restoration at Federal facilities. Further improvement in the efficiency and effectiveness of cleanup programs is necessary, however, if we are to meet public expectations for adequate safeguarding of human health and the environment, and environmental cleanup of Federal facilities and lands. Continued vigorous implementation of management reforms, development of an innovative technologies strategy, statutory, administrative, and regulatory changes, as well as stabilized funding, will all be necessary if we are to accomplish this goal within constrained resources. Federal facility restoration cannot be accomplished by the Federal government working alone. Continued productive collaboration among all stakeholders is essential for long-term success.
GLOSSARY
Active Site - A potentially contaminated site where an investigation or remedial action is currently underway.
Applicable or Relevant and Appropriate Requirements (ARARs) - A CERCLA term for any additional cleanup standards (including State environmental requirements and other Federal standards or criteria) which the Environmental Protection Agency or State regulators may impose in selecting the ultimate remedy for a contaminated site.
Appropriated Funds - Funds made available, through Congressional appropriations acts or other laws, which permit the Government to incur obligations and make payments.
Assessment - See "Characterization."
Base Realignment and Closure (BRAC) Account - The account from which Congress requires the Department of Defense to fund environmental restoration efforts at military installations being closed or realigned. The BRAC environmental program, part of an overall BRAC account, funds more than environmental restoration efforts; it also includes environmental compliance and planning related to the closure of military installations.
Bioremediation - Techniques using biological processes to treat contaminated soil or groundwater. Bioremediation can occur either in situ (i.e., on site) or in bioreactors where contaminated media are placed in contact with organisms to degrade the contaminants in a controlled environment. Generally, the technique involves stimulating organisms by adding materials such as nutrients or oxygen to increase the rate of biodegradation.
Budget, Actual - The amount of funding Congress actually appropriates for spending in a given fiscal year.
Budget, Enacted - This is the same as the "actual budget" -- the amount of funding Congress actually enacts through appropriations laws for spending in a given fiscal year.
Budget Request - The amount of funding the President requests the Congress appropriate in a given fiscal year. In formulating the President's budget request, the Administration identifies its major funding themes and crosscutting issues and then makes decisions on agency budget requests, based on Presidential priorities, program performance, and budget constraints.
Budget Target - The amount of a given fiscal year's discretionary funding apportioned to each Federal agency, based on anticipated levels of appropriations. Agencies are expected to adhere to this target in their budget request to the Administration.
Cap - An impermeable earthen or concrete barrier used in environmental restoration. A cap is placed over a contaminated site to prevent further spread of contaminants through groundwater movement.
CERCLA - See "Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act."
Characterization - Site sampling, monitoring, and analysis to determine the extent and nature of releases. Characterization provides the basis for acquiring the necessary technical information to develop, screen, analyze, and select appropriate cleanup techniques.
Civil Penalties - Financial or administrative penalties assessed on an entity for its failure to comply with legal requirements.
Community Environmental Response Facilitation Act (CERFA) - A Federal law which requires the Department of Defense to identify uncontaminated parcels of land or property that can be quickly turned over to communities for economic reuse. CERFA amends CERCLA, allowing 18 months to identify, document, and concur on all uncontaminated parcels of land or property at military installations undergoing closure.
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act - A Federal law, enacted in 1980, that governs the cleanup of hazardous, toxic, and radioactive substances. The Act and its amendments created a trust fund, commonly known as Superfund, to finance the investigation and cleanup of abandoned and uncontrolled hazardous waste sites. Also commonly referred to by its acronym, CERCLA.
Constant Dollars - A budget term which indicates that outyear costs calculated from a set time baseline do not incorporate the time value of money, such as the effects of inflation. When using, the current year as the time baseline, this is the same as "current dollars."
Contingency Costs - Costs added to the base cost of performing a specific work scope to cover potential deviations from that work scope.
Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) - The mechanism through which the Federal government funds research and development of promising technologies.
Corrective Action - Actions under RCRA or comparable State hazardous waste laws that require a permitted or interim status, hazardous waste management facility to identity and remediate hazardous waste releases from both active and inactive historic activities. Corrective Action Orders can suspend or revoke the authority to operate a treatment, storage, or disposal facility.
Cost-Benefit Analysis - An analysis of the cost of an activity and the benefits (quantitative and/or qualitative) which would accrue from that activity. Used as a decision making tool to determine whether or not to pursue the activity.
Cost-Plus-Award-Fee Contract - A contract which compensates a contractor for costs incurred to perform the contract work scope and also pays both a fixed "base fee" and a fee based on the contractor's performance (an incentive to perform well). Department of Energy management and operating contracts have historically been cost-plus-award-fee contracts.
Cost-Reimbursement Contract - Also known as a cost-plus-no-fee contract, this contract reimburses a contractor for incurred costs; there is no additional fee offered to the contractor.
Crib - A buried structure, often of wood or concrete, filled with aggregate. Its function is to hold or disperse low-level liquids and of solutions for percolation into the ground.
Criminal Liability - The risk of being prosecuted, fined, and jailed for an act which violates a legal requirement.
Current Dollars - A budget term which indicates that outyear costs calculated from the current year do not incorporate the time value of money, such as the effects of inflation.
Deactivation - The removal of hazards from a facility in order to bring it to a safe shutdown, with a focus on minimizing surveillance and maintenance until it can be decontaminated and decommissioned.
Decay (Radioactive) - The spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of an unstable atom, resulting in the emission of particles and energy.
Decommissioning - The process of removing a facility from operation. This retirement of a facility includes decontamination and/or dismantlement.
Decontamination - The removal of unwanted radioactive material from plants, soil, or equipment by chemical or mechanical processes or other techniques.
Defense Authorization Act - The act through which Congress authorizes appropriations for the Department of Defense and Department of Energy.
Direct Costs - Those costs directly attributable to performing core program objectives, as opposed to indirect costs such as for administrative support and infrastructure maintenance.
Discretionary Funds - The category of U.S. government budget authority from which all Federal facility environmental programs are funded. The President and Congress must decide how to spend this money; and Congress allocates these funds through appropriations acts. All other U.S. government funding is mandatory and includes entitlements (such as Social Security, Medicare, and Food Stamps) and interest on the national debt.
Disposal - Waste emplacement designed to ensure isolation of the waste from the biosphere, with no intention of retrieval for the foreseeable future, and requiring deliberate action to regain access to the waste.
Economic Redevelopment - The economically sustainable reuse/redevelopment of a formerly contaminated Federal facility for other than Federal missions.
Environmental Impact Statements - A study prepared in accordance with National Environmental Policy Act guidelines. These studies evaluate and compare the environmental consequences of a proposed major action, such as the construction of a new facility or other alternatives to that action. The conclusion of an environmental impact statement is usually a record of decision to select the preferred alternative.
Environmental Justice - The principle, as stated in Executive Order 12898, that Federal programs, policies, and activities should not pose disproportionately high and adverse human health or environmental effects on minority and low-income populations.
Environmental Restoration - The cleanup, to accepted levels, of sites contaminated with hazardous substances.
Executive Order - A rule or order having the force of law, issued by the President.
Federal Facilities Compliance Act (FFCA) - A 1992 Federal law which requires the Federal government to develop plans to dispose of Federal facilities' mixed wastes and which waives sovereign immunity from civil penalties for violations of Federal, State, and local hazardous waste laws, and allows the use of administrative enforcement authorities under those laws.
Fissile Material - Material capable of being split by a low-energy neutron. The most common fissile materials are uranium 235 and plutonium 239.
Fixed-Price Contract - A contract for goods or services in which a contractor receives a firm, fixed price to perform the contracted work scope. Because any additions to the work scope result in additional payments to the contractor, these contracts are most suitable for routine or well defined scopes of work.
Force Majeure - Those events which, by their uncontrollable nature, legally nullify and void commitments made. In environmental cleanup, failure of Congress to appropriate sufficient funds to allow the Federal government to meet its legal cleanup commitments is often termed a "force majeure," which would require renegotiation of commitments.
Formerly Used Defense Sites (FUDS) - FUDS are properties formerly owned by, leased to, used by, or otherwise under the operational control of the Department of Defense.
FTE (Full-Time Equivalent) Employment - The basic measure of the levels of U.S. government employment. It is the number of hours worked (or to be worked) divided by the total number of compensable hours in a fiscal year.
Future Land Use - The present day determination of how currently contaminated lands will be used in the future (e.g., residential, recreational, industrial uses). Used to assist in setting in order to decide appropriate cleanup levels.
Geologic Repository - A mined facility for disposal of radioactive waste that uses natural geologic barriers to provide waste containment for geologic time periods (millions of years).
Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA) - A 1993 Federal law which requires government-wide performance measurement, budgeting and results monitoring.
Groundwater - Water occurring beneath the earth's surface that supplies wells and springs.
Half-Life - The time it takes for one-half of any given number of unstable atoms to decay. Each isotope has its own characteristic half-life. They range from small fractions of a second to billions of years (the half-life for plutonium is 24,000 years).
Hazardous Waste - As defined in RCRA, a solid waste, or combination of solid wastes, that because of its quantity, concentration, or physical, chemical, or infectious characteristics, may cause or significantly contribute to an increase in mortality or an increase in serious, irreversible, or incapacitating reversible illness or pose a substantial present or potential hazard to human health or the environment when improperly treated, stored, transported, or disposed of, or otherwise managed.
Health Physics - The science of radiation protection.
Highly Enriched Uranium (HEU) - Uranium with more than 20 percent of the uranium 235 isotope, used for making nuclear weapons and also as fuel for some isotope-production, research, and power reactors. Weapons-grade uranium is a subset of this group.
High-Level Waste - Material generated by chemical reprocessing of spent fuel and irradiated targets. High-level waste contains highly radioactive, short-lived fission products, hazardous chemicals, and toxic heavy metals. High-level waste is usually found in the form of a liquid, a solid saltcake, a sludge, or a dry powdery calcine.
Impermeable Barrier - A durable material (usually clay or a geotextile) which serves as a barrier to contaminant and water movement.
Indirect Costs - Costs not related to achieving core program objectives; it includes such sitewide costs as administrative support, utilities, infrastructure maintenance, and security.
Injunctive Relief - The ability to order an entity to refrain from doing a specified act. In Federal cleanup, State and local regulators have the ability to seek injunctive relief against a Federal agency, ordering the agency to stop activities which violate environmental laws.
Innovative Technology - A technology considered promising but not yet demonstrated sufficiently to be considered proven and thus widely used for cleanups.
In Situ Remediation - Any environmental remediation technique which is applied at the site of the contamination, rather than moving the contaminants to a separate treatment facility.
Interagency Agreements (IAGS) - Legally binding agreements between regulatory agencies and regulated parties setting standards and schedules (marked by milestone activities) for compliance with environmental laws. CERCLA requires IAGs for all sites on the National Priorities List.
Interim Action - Removal actions and interim remedial actions that accelerate the reduction of risk to human health and the environment. Interim actions remove or stabilize contaminant sources and thereby reduce or eliminate immediate risks until final remediation.
Ionizing Radiation - Radiation that is capable of breaking apart molecules or atoms. The splitting or decay of unstable atoms typically emits ionizing radiation.
Isotopes - Different forms of the same chemical element that differ only by the number of neutrons in their nucleus. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope. Many more isotopes have been produced in reactors and scientific laboratories.
Leaching - The passing of a soluble constituent or contaminant through a permeable substance, such as soil.
Legacy Waste - Waste products generated during the Department of Energy's production of nuclear weapons from 1943 until 1989. The Department's Environmental Management Program is responsible for cleaning up, treating and disposing of this legacy waste, much of which has simply been stored for the past 50 years.
Low-Enriched Uranium. Uranium that has been enriched until it consists of about 3 percent uranium 235 and 97 percent uranium 238. Used as nuclear reactor fuel.
Low-Level Waste. A catchall term for any radioactive waste that is not spent fuel, high-level, or transuranic waste.
"Make or Buy" - A decision as to whether to produce (make) or to purchase (buy) goods or services, based on an analysis of costs and long-term strategic objectives.
Management and Operating (M&O) Contractor - Contractors hired by the Department of Energy to manage and operate its sites, including research and development laboratories and nuclear weapons production facilities.
Milestones - See "Interagency Agreements."
Mine Tailings - The materials left over from separating a recoverable resource from its ore.
Mixed Waste - Waste that contains both chemically hazardous and radioactive materials.
Municipal Waste - Waste generated from typical residential and light industrial operations.
Munitions - Any type of explosive military ammunition (as in grenades or bombs).
National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) - A Federal law, enacted in 1970, that requires the Federal government to consider the environmental impacts of, and alternatives to, major proposed actions in its decision-making processes. Commonly referred to by its acronym, NEPA.
National Performance Review - A March 1993 Clinton Administration initiative to review and recommend changes to the Federal government, to create a more effective, efficient and responsive government that works better and costs less.
National Priorities List (NPL) - A listing of the nation's worst hazardous waste sites requiring cleanup, as established by CERCLA.
Natural Resource Damage - Damage to ecological resources from environmental contamination. The Federal government has not completed many assessments to quantify the impacts on and risks to these ecological resources, since Federal funding to date has been primarily focused on human health and safety rather than ecological risks.
Natural Uranium. Uranium that has not been through the enrichment process. It is made of 99.3 percent uranium 238 and 0.7 percent uranium 235.
Non-Legacy Waste - As distinguished from legacy waste, those waste products generated from the Department of Energy's operations after nuclear weapons production stopped in 1989.
Nonproliferation - Efforts to prevent or slow the spread of nuclear weapons and the materials and technologies used to produce them.
Nuclear Weapons Complex - The chain of foundries, uranium enrichment plants, reactors, chemical separation plants, factories, laboratories, assembly plants, and test sites that produced nuclear weapons. There are 16 major facilities in the U.S. nuclear weapons complex that are located in 12 states.
Obligation (Funding) - A binding agreement that will result in Government spending either immediately or in the future. Budgetary resources must be available before obligations can be legally incurred.
Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA) - A Federal law, passed in 1993, which caps Federal discretionary spending through 1998.
Operable Unit - A discrete area consisting of a single to many potential release sites, grouped together for purposes of assessment and cleanup. The primary criteria for placement of release sites into an operable unit include geographic proximity, similarity of waste characteristics and site type, and the possibility for economies of scale.
Ordnance - Military weapons of all kinds, including associated equipment and ammunition.
Overhead Costs - Those costs, such as administrative support and infrastructure maintenance, not directly chargeable to a particular work element.
Phytoremediation - The emerging science of planting specific crops which draw into their root systems comparatively large quantities of contaminants from soils or water and, over time and successive plantings, can remediate the environmental impact of contaminants.
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBS) - A group of commercially produced organic chemicals used extensively since the 1940s in industrial applications at Federal facilities. Most notably, PCBs are found in gaskets, large electrical transformers, and capacitors. PCBs have been proven to be toxic to both humans and laboratory animals.
Plutonium - A manmade fissile element. Pure plutonium is a silvery metal that is heavier than lead. Material rich in the Plutonium 239 isotope is preferred for manufacturing nuclear weapons, although any plutonium can be used. Plutonium 239 has a half-life of 24,000 years.
Potential Release Site - A site from which there is a potential for release of contaminants to the environment -- for example, a hazardous waste storage tank.
Preliminary Assessments - A phase of the CERCLA remediation process used to determine whether a site has contaminated, or has the potential to contaminate, the environment.
Presumptive Remedy - A remedial action alternative selected based on the remedy's successful use on similar past cleanups, in order to expedite the CERCLA remedial investigation process.
Privatization - The conversion of a government-performed activity to private non-government performance, either to eliminate an activity which is not a valid government function or to cut the cost or improve the efficiency of performing the activity by introducing competition.
Procurement - The process through which the Federal government contracts for goods or services from outside sources.
Pump and Treat - Groundwater remediation technique involving the extraction of contaminated groundwater from the subsurface to remove contaminants and subsequent return of the treated water to its source.
Radioactive Waste - Solid, liquid, or gaseous material resulting from weapons production that contains radionuclides in excess of threshold quantities. This may include high level, low level, or transuranic wastes, spent fuels, or highly enriched uranium.
Radionuclide - A radioactive species of an atom. For example, tritium, strontium 90, and uranium 235 are all radionuclides.
RCRA - See "Resource Conservation and Recovery Act."
Record of Decision (ROD) - The CERCLA document which selects the remedial action to be implemented at a site after the Remedial Investigation and Feasibility Study is completed.
Reinventing Government (REGO) - A continuation of Federal agency initiatives begun under the National Performance Review.
Remedial Investigation and Feasibility Study (RI/FS) - A phase of the CERCLA remediation process to identify the nature and extent of contamination at a site, and to evaluate remedial action alternatives to correct or prevent the migration of those contaminants from that site.
Remediation - The process of applying a chosen technique or process to correct an environmental problem. This process may either stabilize, contain, entomb, neutralize, or destroy the hazardous contaminant.
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act - A Federal law enacted in 1976 to address the treatment, storage, and disposal of hazardous waste.
Restoration - See "Environmental Restoration"
Restoration Advisory Board (RAB) - The mechanism through which the Department of Defense involves its local stakeholders in Federal cleanup decisions.
Risk Assessment - A methodology to evaluate the extent of human exposure to environmental contaminants with potential health effects. Risk assessments may be quantitative (calculated from exposure to a contaminant and its known chemical characteristics) or qualitative (taking into account cultural, social, and economic factors, including environmental justice considerations).
Rule Making - The process through which a Federal agency promulgates rules or regulations to implement laws passed by Congress. The Code of Federal Regulations publishes all such rules.
Sequestration of Funds - The cancellation of discretionary funds which could be appropriated. This occurs to keep spending within preauthorized limits.
Site Characterization - The technical process used to evaluate the nature and extent of environmental contamination. This process is necessary for designing remediation measures and monitoring their effectiveness.
Sovereign Immunity - The Constitutional principle that the Federal Government is not required to comply with any laws unless Congress specifically waives immunity to that law. The Federal Facilities Compliance Act amended RCRA's waiver of sovereign immunity, to hold Federal agencies liable for civil penalties and Federal officials liable for criminal sanctions.
Spent Nuclear Fuel - Fuel elements and other materials (such as uranium 238 "targets" used to produce plutonium) that have been irradiated in a nuclear reactor.
Stakeholders - Individuals, or groups of individuals, interested in or affected by agency operations or cleanup activities.
Superfund - See "Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act."
Support Services - Those discrete services, ranging from routine tasks (such as clerical support and moving services) to highly specialized technical tasks, which the Department of Energy contracts for, rather than hiring permanent Federal employees.
Toxicity - The ability of a substance to cause damage to living tissue- impairment of the central nervous system; severe illness; or (in extreme cases) death when ingested, inhaled, or absorbed by the skin. Amounts required to produce these results vary widely with the nature of the substances and the time of exposure.
Transport Mechanisms - The various ways contaminants can spread, e.g., through air, groundwater, etc.
Transuranic Waste - Radioactive waste contaminated with uranium 233 or elements beyond uranium on the periodic table and existing, in concentrations of more than 1 ten-millionth of a curie per gram of waste. These isotopes have half-lives of over 20 years and are all man made.
Treatment Facility - A facility in which activities are performed that alter the chemical or physical nature of a hazardous waste to reduce its toxicity, volume, mobility, or render it amenable for transport, storage, or disposal.
Uranium - The basic material for nuclear technology, it is a slightly radioactive, naturally occurring heavy metal that is more dense than lead.
Vitrification - A process that stabilizes nuclear waste by mixing it with molten glass. The glass is poured into metal canisters, where it hardens into logs. The Department of Energy has built plants for vitrifying high-level-waste at West Valley, New York, and the Savannah River Site.
Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) - A geologic repository intended to provide permanent disposal for transuranic wastes, deep underground (2,150 feet) in a salt bed near Carlsbad, New Mexico.
Watershed - The land mass over which all surface water runs into a
particular body of water.
| Back to Top | |
| FFRRO Home | EPA Home |
| FFRRO Partnerships | |